Undernutrition and stage of gestation influence fetal adipose tissue gene expression
- PMID: 25917833
- PMCID: PMC4449808
- DOI: 10.1530/JME-15-0048
Undernutrition and stage of gestation influence fetal adipose tissue gene expression
Abstract
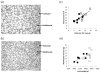
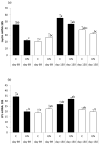
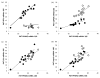
Low birthweight is a risk factor for neonatal mortality and adverse metabolic health, both of which are associated with inadequate prenatal adipose tissue development. In the present study, we investigated the impact of maternal undernutrition on the expression of genes that regulate fetal perirenal adipose tissue (PAT) development and function at gestation days 89 and 130 (term=145 days). Singleton fetuses were taken from adolescent ewes that were either fed control (C) intake to maintain adiposity throughout pregnancy or were undernourished (UN) to maintain conception weight but deplete maternal reserves (n=7/group). Fetal weight was independent of maternal intake at day 89, but by day 130, fetuses from UN dams were 17% lighter and had lower PAT mass that contained fewer unilocular adipocytes. Relative PAT expression of IGF1, IGF2, IGF2R and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) mRNA was lower in UN than in controls, predominantly at day 89. Independent of maternal nutrition, PAT gene expression of PPARG, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, hormone sensitive lipase, leptin, uncoupling protein 1 and prolactin receptor increased, whereas IGF1, IGF2, IGF1R and IGF2R decreased between days 89 and 130. Fatty acid synthase and lipoprotein lipase (LPL) mRNAs were not influenced by nutrition or stage of pregnancy. Females had greater LPL and leptin mRNA than males, and LPL, leptin and PPARG mRNAs were decreased in UN at day 89 in females only. PAT gene expression correlations with PAT mass were stronger at day 89 than they were at day 130. These data suggest that the key genes that regulate adipose tissue development and function are active beginning in mid-gestation, at which point they are sensitive to maternal undernutrition: this leads to reduced fetal adiposity by late pregnancy.
Keywords: adipose tissue; fetal; gene expression; sheep; undernutrition.
© 2015 Society for Endocrinology.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors had any financial or personal conflicts of interest.
Figures
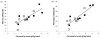
References
-
- AFRC. An Advisory Manual Prepared by the AFRC Technical Committee on Responses to Nutrients. Wallingford: CAB International; 1993. Energy and Protein Requirements of Ruminants.
-
- Bispham J, Gopalakrishnan GS, Dandrea J, Wilson V, Budge H, Keisler DH, Broughton Pipkin F, Stephenson T, Symonds ME. Maternal endocrine adaptation throughout pregnancy to nutritional manipulation: consequences for maternal plasma leptin and cortisol and the programming of fetal adipose tissue development. Endocrinology. 2003;144:3575–3585. - PubMed
-
- Budge H, Edwards LJ, McMillan IC, Bryce A, Warnes K, Pearce S, Stephenson T, Symonds ME. Nutritional manipulation of fetal adipose deposition and uncoupling protein 1 messenger RNA abundance in the sheep: differential effects of timing and duration. Biology of Reproduction. 2004;71:359–365. - PubMed
-
- Cagnacci A, Arangino S, Caretto S, Mazza V, Volpe A. Sexual dimorphism in the levels of amniotic fluid leptin in pregnancies at 16 weeks gestation: relation to fetal growth. European Journal of Obstetrics Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. 2006;124:53–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

