[Persistence of hepatitis A virus antibodies after primary immunization and response to revaccination in children and adolescents with perinatal HIV exposure]
- PMID: 25918013
- PMCID: PMC4516366
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpped.2014.09.005
[Persistence of hepatitis A virus antibodies after primary immunization and response to revaccination in children and adolescents with perinatal HIV exposure]
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:: To assess possible factors associated with the loss of antibodies to hepatitis A 7 years after the primary immunization in children of HIV-infected mothers and the response to revaccination in patients seronegative for hepatitis A.
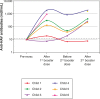
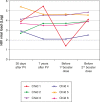
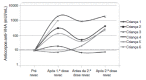
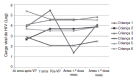
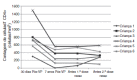
METHODS:: Quantification of HAV antibodies by electrochemiluminescence was performed in 39 adolescents followed up at the Pediatric Aids Clinic of Federal University of São Paulo (Unifesp): 29 HIV-infected (HIV group) (median age: 12.8 years) and 10 HIV-exposed but non-infected (ENI group) (median age: 13.4 years). All of them received two doses of HAV vaccine (Havrix(r)) in 2002.
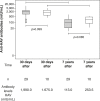
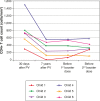
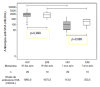
RESULTS:: The median age at primary immunization (PI) was 5.4 years for HIV group and 6.5 years for ENI group. All children, from both groups, had antibodies to HAV >20 mIU/mL after PI. Seven years later, the ENI group showed a median concentration of antibodies = 253.5 mIU/mL, while the HIV group = 113.0 mIU/mL (Mann-Whitney test, p=0.085). All ENI group and 23/29 (79.3%) from HIV group mantained HAV antibodies 7 years after PI. The levels of hepatitis A antibodies in the primary vaccination were the only factor independently associated with maintaining these antibodies for 7 years. The group that lost HAV seropositivity was revaccinated and 83.3% (5/6) responded with antibodies >20 mUI/mL.
CONCLUSIONS:: The antibodies levels acquired in the primary vaccination in the HIV group were the main factor associated with antibodies loss after HAV immunization.
Keywords: Adolescent and children; Crianças e adolescentes; HIV; Hepatitis A vaccine; Immunossupression; Imunossupressão; Vacina de hepatite A.
Copyright © 2015 Associação de Pediatria de São Paulo. Publicado por Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Brady MT, Oleske JM, Williams PL, Elgie C, Mofenson LM, Dankner WM, et al. Declines in mortality rates and changes in causes of death in HIV-1-infected children during the HAART era. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;53:86-94. - PMC - PubMed
- Brady MT, Oleske JM, Williams PL, Elgie C, Mofenson LM, Dankner WM. Declines in mortality rates and changes in causes of death in HIV-1-infected children during the HAART era. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;53:86–94. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matida LH, Ramos AN Jr, Heukelbach J, Hearst N, Brazilian Study Group on Survival of Children with Aids. Continuing improvement in survival for children with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in Brazil. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28:920-2. - PubMed
- Matida LH, Ramos AN, Jr, Heukelbach J, Hearst N, Brazilian Study Group on Survival of Children with Aids Continuing improvement in survival for children with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in Brazil. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28:920–922. - PubMed
-
- Costa-Mattioli M, Allavena C, Poirier AS, Billaudel S, Raffi F, Ferré V. Prolonged hepatitis A infection in an HIV-1 seropositive patient. J Med Virol. 2002;68:7-11. - PubMed
- Costa-Mattioli M, Allavena C, Poirier AS, Billaudel S, Raffi F, Ferré V. Prolonged hepatitis A infection in an HIV-1 seropositive patient. J Med Virol. 2002;68:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Ridolfo AL, Rusconi S, Antinori S, Balotta C, Galli M. Persisting HIV-1 replication triggered by acute hepatitis A virus infection. Antivir Ther. 2000;5:15-7. - PubMed
- Ridolfo AL, Rusconi S, Antinori S, Balotta C, Galli M. Persisting HIV-1 replication triggered by acute hepatitis A virus infection. Antivir Ther. 2000;5:15–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

