RWD Domain as an E2 (Ubc9)-Interaction Module
- PMID: 25918163
- PMCID: PMC4505409
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.644047
RWD Domain as an E2 (Ubc9)-Interaction Module
Abstract
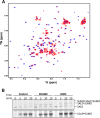
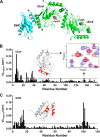
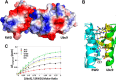
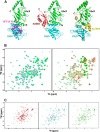
An RWD domain is a well conserved domain found through bioinformatic analysis of the human proteome sequence; however, its function has been unknown. Ubiquitin-like modifications require the catalysis of three enzymes generally known as E1, E2, and E3. We solved the crystal structure of the E2 for the small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMO) in complex with an RWD domain and confirmed the structure using solution NMR analysis. The binding surface of RWD on Ubc9 is located near the N terminus of Ubc9 that is known to be involved in noncovalent binding of the proteins in the conjugation machinery, including a domain of E1, SUMO, and an E3 ligase. NMR data indicate that the RWD domain does not bind to SUMO and E1. The interaction between RWD and Ubc9 has a Kd of 32 ± 4 μM. Consistent with the structure and binding affinity and in contrast to a previous report, the RWD domain and RWDD3 have minimal effects on global SUMOylation. The structural and biochemical information presented here forms the basis for further investigation of the functions of RWD-containing proteins.
Keywords: E2; RWD; nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO); sumoylation; ubiquitylation (ubiquitination); x-ray crystallography.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
Function and Structure of the RWD Domain.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 14;290(33):20627. doi: 10.1074/jbc.L115.669382. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26276859 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Function and Structure of the RWD Domain.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 14;290(33):20628. doi: 10.1074/jbc.l115.677229. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26495453 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Carbia-Nagashima A., Gerez J., Perez-Castro C., Paez-Pereda M., Silberstein S., Stalla G. K., Holsboer F., Arzt E. (2007) RSUME, a small RWD-containing protein, enhances SUMO conjugation and stabilizes HIF-1alpha during hypoxia. Cell 131, 309–323 - PubMed
-
- Ulrich H. D. (2009) The SUMO system: an overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 497, 3–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

