Alpha-actinin binding kinetics modulate cellular dynamics and force generation
- PMID: 25918384
- PMCID: PMC4450414
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1505652112
Alpha-actinin binding kinetics modulate cellular dynamics and force generation
Abstract
The actin cytoskeleton is a key element of cell structure and movement whose properties are determined by a host of accessory proteins. Actin cross-linking proteins create a connected network from individual actin filaments, and though the mechanical effects of cross-linker binding affinity on actin networks have been investigated in reconstituted systems, their impact on cellular forces is unknown. Here we show that the binding affinity of the actin cross-linker α-actinin 4 (ACTN4) in cells modulates cytoplasmic mobility, cellular movement, and traction forces. Using fluorescence recovery after photobleaching, we show that an ACTN4 mutation that causes human kidney disease roughly triples the wild-type binding affinity of ACTN4 to F-actin in cells, increasing the dissociation time from 29 ± 13 to 86 ± 29 s. This increased affinity creates a less dynamic cytoplasm, as demonstrated by reduced intracellular microsphere movement, and an approximate halving of cell speed. Surprisingly, these less motile cells generate larger forces. Using traction force microscopy, we show that increased binding affinity of ACTN4 increases the average contractile stress (from 1.8 ± 0.7 to 4.7 ± 0.5 kPa), and the average strain energy (0.4 ± 0.2 to 2.1 ± 0.4 pJ). We speculate that these changes may be explained by an increased solid-like nature of the cytoskeleton, where myosin activity is more partitioned into tension and less is dissipated through filament sliding. These findings demonstrate the impact of cross-linker point mutations on cell dynamics and forces, and suggest mechanisms by which such physical defects lead to human disease.
Keywords: Alpha-actinin; actin; cell mechanics; kidney disease; traction force.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
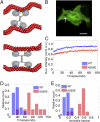
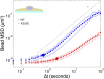
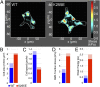

Comment in
-
Dynamic cross-links tune the solid-fluid behavior of living cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 26;112(21):6527-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1507100112. Epub 2015 May 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26015553 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Congenital macrothrombocytopenia-linked mutations in the actin-binding domain of α-actinin-1 enhance F-actin association.FEBS Lett. 2016 Mar;590(6):685-95. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12101. Epub 2016 Mar 1. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 26879394
-
Nonlinear viscoelasticity of actin transiently cross-linked with mutant α-actinin-4.J Mol Biol. 2011 Sep 2;411(5):1062-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.06.049. Epub 2011 Jul 6. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21762701 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of alpha-actinin 4 upon epidermal growth factor exposure regulates its interaction with actin.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 22;285(4):2591-600. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.035790. Epub 2009 Nov 17. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19920151 Free PMC article.
-
The fifth sense: Mechanosensory regulation of alpha-actinin-4 and its relevance for cancer metastasis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Nov;71:68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.05.024. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28579451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-actinin 4 and tumorigenesis of breast cancer.Vitam Horm. 2013;93:323-51. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416673-8.00005-8. Vitam Horm. 2013. PMID: 23810014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SERPINE1 Gene Is a Reliable Molecular Marker for the Early Diagnosis of Aortic Dissection.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 5;2022:5433868. doi: 10.1155/2022/5433868. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9878327. doi: 10.1155/2023/9878327. PMID: 35836829 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Response of biopolymer networks governed by the physical properties of cross-linking molecules.Soft Matter. 2016 Mar 7;12(9):2537-41. doi: 10.1039/c5sm02820e. Soft Matter. 2016. PMID: 26760315 Free PMC article.
-
Traction Force Screening Enabled by Compliant PDMS Elastomers.Biophys J. 2018 May 8;114(9):2194-2199. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.02.045. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29742412 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking fast cellular membrane dynamics with sub-nm accuracy in the normal direction.Nanoscale. 2018 Mar 15;10(11):5133-5139. doi: 10.1039/c7nr09483c. Nanoscale. 2018. PMID: 29488990 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-actinin 4 and tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Aug;8(4):1374-1380. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.07.34. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116880 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

