Lifelong parental voluntary wheel running increases offspring hippocampal Pgc-1α mRNA expression but not mitochondrial content or Bdnf expression
- PMID: 25919993
- PMCID: PMC4416227
- DOI: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000371
Lifelong parental voluntary wheel running increases offspring hippocampal Pgc-1α mRNA expression but not mitochondrial content or Bdnf expression
Abstract
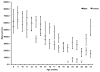
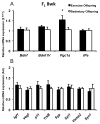
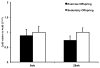
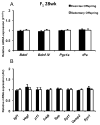
When exercise is initiated during pregnancy, offspring of physically active mothers have higher hippocampal expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) and other plasticity-associated and mitochondria-associated genes, resulting in hippocampal structural and functional adaptations. In the present study, we examined the effects of lifelong parental voluntary wheel running (before, during, and after pregnancy) on offspring hippocampal mRNA expression of genes implicated in the exercise-induced improvement of cognitive function. C57BL/6 mice were individually housed at 8 weeks of age with (EX, n=20) or without (SED, n=20) access to a computer-monitored voluntary running wheel for 12 weeks before breeding. EX breeders maintained access to the voluntary running wheel throughout breeding, pregnancy, and lactation. Male offspring were housed in sedentary cages, regardless of the parental group, and were killed at 8 (n=18) or 28 weeks (n=19). PCR was used to assess mRNA expression of several genes and mitochondrial content (ratio of mitochondrial to nuclear DNA) in hippocampal homogenates. We found significantly higher peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1 α (Pgc-1α) mRNA expression in EX offspring compared with SED offspring at 8 weeks (P=0.04), although the effect was no longer present at 28 weeks. There was no difference in mitochondrial content or expression of Bdnf or any other mRNA target between offspring at 8 and 28 weeks. In contrast to exercise initiated during pregnancy, parental voluntary physical activity initiated early in life and maintained throughout pregnancy has little effect on offspring mRNA expression of genes implicated in exercise-induced hippocampal plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex-dependent and independent effects of long-term voluntary wheel running on Bdnf mRNA and protein expression.Physiol Behav. 2016 Mar 15;156:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.12.026. Epub 2016 Jan 2. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 26752611 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy activation, not peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α, may mediate exercise-induced improvements in glucose handling during diet-induced obesity.Exp Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;102(9):1194-1207. doi: 10.1113/EP086406. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Exp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28639297
-
Short-term running exercise alters DNA methylation patterns in neuronal nitric oxide synthase and brain-derived neurotrophic factor genes in the mouse hippocampus and reduces anxiety-like behaviors.FASEB J. 2021 Aug;35(8):e21767. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100630R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34325488
-
Sex-dependent effects of chronic exercise on cognitive flexibility but not hippocampal Bdnf in aging mice.Neuronal Signal. 2022 Jan 5;6(1):NS20210053. doi: 10.1042/NS20210053. eCollection 2022 Apr. Neuronal Signal. 2022. PMID: 35036000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between BDNF and PGC-1 alpha in maintaining brain health: role of exercise.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 22;15:1433750. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1433750. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39239097 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A single bout of exercise increases hippocampal Bdnf: influence of chronic exercise and noradrenaline.Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Nov;16(8):800-811. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12394. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Genes Brain Behav. 2017. PMID: 28556463 Free PMC article.
-
Paternal physical exercise modulates global DNA methylation status in the hippocampus of male rat offspring.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Mar;14(3):491-500. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.245473. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30539818 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-dependent and independent effects of long-term voluntary wheel running on Bdnf mRNA and protein expression.Physiol Behav. 2016 Mar 15;156:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.12.026. Epub 2016 Jan 2. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 26752611 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise alters mouse sperm small noncoding RNAs and induces a transgenerational modification of male offspring conditioned fear and anxiety.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 May 2;7(5):e1114. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.82. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28463242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clapp JF., III Exercise during pregnancy: a clinical update. Clinics in sports medicine. 2000 - PubMed
-
- Committee OPAGA. US Department of Health and Human Services and Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee. 2008:1–683.
-
- Parnpiansil P. Exercise during pregnancy increases hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression and spatial learning in neonatal rat pup. Neuroscience Letters. 2003 - PubMed
-
- Lee H-H, Kim H, Lee J-W, Kim Y-S, Yang H-Y, Chang H-K, et al. Maternal swimming during pregnancy enhances short-term memory and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of rat pups. Brain and Development. 2006;28(3):147–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

