Treatment of acute relapses in neuromyelitis optica: Steroids alone versus steroids plus plasma exchange
- PMID: 25921047
- PMCID: PMC4795457
- DOI: 10.1177/1352458515581438
Treatment of acute relapses in neuromyelitis optica: Steroids alone versus steroids plus plasma exchange
Abstract
Background: Although adding plasma exchange (PLEX) to steroids in severe neuromyelitis optica (NMO) attacks is common practice in steroid-resistant cases, the benefit of this strategy has not been previously quantified.
Objective: The objective of this paper is to compare the efficacy of high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone (IVMP) versus IVMP+PLEX in treatment of acute NMO relapses.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of the last 83 NMO admissions to the Johns Hopkins Hospital treated with IVMP alone versus IVMP+PLEX (for steroid-resistant cases). Extended Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score was calculated at baseline, at presentation, at discharge, and on follow-up.
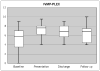
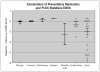
Results: Eighteen NMO relapses (16 patients, 87% female, mean age at relapse: 33.9±23.8, median baseline EDSS 2.5) were treated with IVMP alone and 65 relapses (43 patients, 95% female, mean age at relapse: 43.8±15.7, median baseline EDSS 5.75) were treated with IVMP + PLEX. Sixty-five percent of IVMP + PLEX patients achieved an EDSS equal or below their baseline at follow-up while only 35% of the IVMP-only patients achieved their baseline EDSS on follow-up (odds ratio=3.36, 95% CI 1.0657 to 10.6004, p = 0.0386). PLEX was more effective in improving EDSS in patients on preventive immunosuppressive medications at time of relapse.
Conclusions: PLEX+IVMP are more likely to improve EDSS after NMO relapses compared to IVMP alone, especially in patients taking preventive medications.
Keywords: EDSS; Neuromyelitis optica; acute relapse; plasma exchange; preventive medications; steroids.
© The Author(s), 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Hesham Abboud has received an educational grant from Teva Pharmaceuticals unrelated to this study. Dr Levy receives research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Guthy Jackson Charitable Foundation, Viropharma, Acorda, Sanofi, NeuralStem and Genentech, and serves as a consultant for Chugai Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline and MedImmune. The other authors have nothing to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Pittock SJ, et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology. 2006;66:1485–1489. - PubMed
-
- Wingerchuk DM, Hogancamp WF, O’Brien PC, et al. The clinical course of neuromyelitis optica (Devic’s syndrome) Neurology. 1999;53:1107–1114. - PubMed
-
- Bichuetti DB, Oliveira EM, Souza NA, et al. Patients with neuromyelitis optica have a more severe disease than patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis, including higher risk of dying of a demyelinating disease. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2013;71:275–279. - PubMed
-
- Wingerchuk DM, Pittock SJ, Lucchinetti CF, et al. A secondary progressive clinical course is uncommon in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology. 2007;68:603–605. - PubMed
-
- Jacob A, McKeon A, Nakashima I, et al. Current concept of neuromyelitis optica (NMO) and NMO spectrum disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 2012;84:922–930. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

