Mitochondrial crisis in cerebrovascular endothelial cells opens the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 25922503
- PMCID: PMC4418219
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009099
Mitochondrial crisis in cerebrovascular endothelial cells opens the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
Background and purpose: The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a selectively permeable cerebrovascular endothelial barrier that maintains homeostasis between the periphery and the central nervous system. BBB disruption is a consequence of ischemic stroke and BBB permeability can be altered by infection/inflammation, but the complex cellular and molecular changes that result in this BBB alteration need to be elucidated to determine mechanisms.
Methods: Infection mimic (lipopolysaccharide) challenge on infarct volume, BBB permeability, infiltrated neutrophils, and functional outcomes after murine transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in vivo; mitochondrial evaluation of cerebrovascular endothelial cells challenged by lipopolysaccharide in vitro; pharmacological inhibition of mitochondria on BBB permeability in vitro and in vivo; the effects of mitochondrial inhibitor on BBB permeability, infarct volume, and functional outcomes after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion.
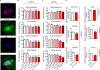
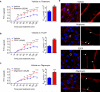
Results: We report here that lipopolysaccharide worsens ischemic stroke outcome and increases BBB permeability after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Furthermore, we elucidate a novel mechanism that compromised mitochondrial function accounts for increased BBB permeability as evidenced by: lipopolysaccharide-induced reductions in oxidative phosphorylation and subunit expression of respiratory chain complexes in cerebrovascular endothelial cells, a compromised BBB permeability induced by pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial function in cerebrovascular endothelial cells in vitro and in an in vivo animal model, and worsened stroke outcomes in transient middle cerebral artery occlusion mice after inhibition of mitochondrial function.
Conclusions: We concluded that mitochondria are key players in BBB permeability. These novel findings suggest a potential new therapeutic strategy for ischemic stroke by endothelial cell mitochondrial regulation.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; mitochondria; stroke.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-149-5p regulates blood-brain barrier permeability after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats by targeting S1PR2 of pericytes.FASEB J. 2018 Jun;32(6):3133-3148. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701121R. Epub 2018 Jan 18. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29401609
-
Microvascular endothelial cells-derived microvesicles imply in ischemic stroke by modulating astrocyte and blood brain barrier function and cerebral blood flow.Mol Brain. 2016 Jun 7;9(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0243-1. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 27267759 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-mediated occludin degradation contributes to blood-brain barrier disruption during ischemia in bEnd.3 brain endothelial cells and rat ischemic stroke models.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020 Mar 14;17(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12987-020-00182-8. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020. PMID: 32169114 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):C343-C356. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00095.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29949404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb 1;316(2):C135-C153. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00136.2018. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30379577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ldlr-/-.Leiden mice develop neurodegeneration, age-dependent astrogliosis and obesity-induced changes in microglia immunophenotype which are partly reversed by complement component 5 neutralizing antibody.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jun 29;17:1205261. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1205261. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37457817 Free PMC article.
-
Immuno-metabolic impact of the multiple sclerosis patients' sera on endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 May 9;17(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01810-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32386505 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Progenitor Cells Modulate Inflammation-Associated Stroke Vasculome.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019 Apr;15(2):256-275. doi: 10.1007/s12015-019-9873-x. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019. PMID: 30739275 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupling of the Electron Transport Chain Compromises Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation and Exacerbates Stroke Outcomes.J Neuroinfect Dis. 2018;9(4):283. doi: 10.4172/2314-7326.1000283. Epub 2018 Dec 31. J Neuroinfect Dis. 2018. PMID: 32149160 Free PMC article.
-
Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 Leads to Inflammatory Activation through NF-κB Non-Canonical Pathway and Mitochondrial Remodeling.Viruses. 2023 Mar 14;15(3):745. doi: 10.3390/v15030745. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubin LL, Staddon JM. The cell biology of the blood-brain barrier. Annual review of neuroscience. 1999;22:11–28. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Avila-Flores A. Maguk proteins: Structure and role in the tight junction. Seminars in cell & developmental biology. 2000;11:315–324. - PubMed
-
- Tajes M, Ramos-Fernandez E, Weng-Jiang X, Bosch-Morato M, Guivernau B, Eraso-Pichot A, et al. The blood-brain barrier: Structure, function and therapeutic approaches to cross it. Molecular membrane biology. 2014;31:152–167. - PubMed
-
- Grau AJ, Buggle F, Heindl S, Steichen-Wiehn C, Banerjee T, Maiwald M, et al. Recent infection as a risk factor for cerebrovascular ischemia. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 1995;26:373–379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

