Sensory hair cell development and regeneration: similarities and differences
- PMID: 25922522
- PMCID: PMC4419275
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.114926
Sensory hair cell development and regeneration: similarities and differences
Abstract
Sensory hair cells are mechanoreceptors of the auditory and vestibular systems and are crucial for hearing and balance. In adult mammals, auditory hair cells are unable to regenerate, and damage to these cells results in permanent hearing loss. By contrast, hair cells in the chick cochlea and the zebrafish lateral line are able to regenerate, prompting studies into the signaling pathways, morphogen gradients and transcription factors that regulate hair cell development and regeneration in various species. Here, we review these findings and discuss how various signaling pathways and factors function to modulate sensory hair cell development and regeneration. By comparing and contrasting development and regeneration, we also highlight the utility and limitations of using defined developmental cues to drive mammalian hair cell regeneration.
Keywords: Atoh1; FGF; Notch; Shh; Wnt; p27Kip1, Cdkn1b.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures


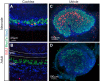
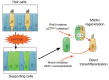
References
-
- Alvarado D. M., Hawkins R. D., Bashiardes S., Veile R. A., Ku Y.-C., Powder K. E., Spriggs M. K., Speck J. D., Warchol M. E. and Lovett M. (2011). An RNA interference-based screen of transcription factor genes identifies pathways necessary for sensory regeneration in the avian inner ear. J. Neurosci. 31, 4535-4543 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5456-10.2011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

