Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms regulating satellite cell function
- PMID: 25922523
- PMCID: PMC4419274
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.114223
Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms regulating satellite cell function
Abstract
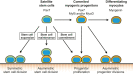
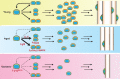
Muscle stem cells, termed satellite cells, are crucial for skeletal muscle growth and regeneration. In healthy adult muscle, satellite cells are quiescent but poised for activation. During muscle regeneration, activated satellite cells transiently re-enter the cell cycle to proliferate and subsequently exit the cell cycle to differentiate or self-renew. Recent studies have demonstrated that satellite cells are heterogeneous and that subpopulations of satellite stem cells are able to perform asymmetric divisions to generate myogenic progenitors or symmetric divisions to expand the satellite cell pool. Thus, a complex balance between extrinsic cues and intrinsic regulatory mechanisms is needed to tightly control satellite cell cycle progression and cell fate determination. Defects in satellite cell regulation or in their niche, as observed in degenerative conditions such as aging, can impair muscle regeneration. Here, we review recent discoveries of the intrinsic and extrinsic factors that regulate satellite cell behaviour in regenerating and degenerating muscles.
Keywords: Aging; Asymmetric division; Cell cycle regulation; Muscle stem cell; Myogenesis; Quiescence; Regeneration; Satellite cell; Self-renewal; Skeletal muscle.
© 2015. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Beauchamp J. R., Heslop L., Yu D. S. W., Tajbakhsh S., Kelly R. G., Wernig A., Buckingham M. E., Partridge T. A. and Zammit P. S. (2000). Expression of Cd34 and Myf5 defines the majority of quiescent adult skeletal muscle satellite cells. J. Cell Biol. 151, 1221-1234 10.1083/jcb.151.6.1221 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

