Prognostic value of different scoring models in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome associated with acute COPD exacerbation
- PMID: 25922710
- PMCID: PMC4387415
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.11.27
Prognostic value of different scoring models in patients with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome associated with acute COPD exacerbation
Abstract
Background and objective: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) represents an increasing healthcare concern as a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Our objective was to predict the outcome of COPD patients associated with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) by scoring models.
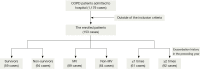
Methods: A retrospective study was performed on severe COPD patients within 24 hours of the onset of MODS. The Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II, APACHE III, Multiple Organ Dysfunction Score (MODS), Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II), and Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores were calculated for patients.
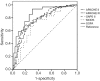
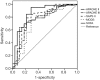
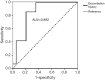
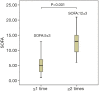
Results: A total of 153 elderly patients were recruited. Compared to 30-day survivors, the number of failing organs and all of the scoring models were significantly higher in 30-day non-survivors. The SOFA showed the highest sensitivity and area under the curve (AUC) for predicting the prognosis of patients with MODS induced by acute exacerbation of COPD. The results of logistic regression indicated that factors that were correlated with the prognosis of COPD included the exacerbation history, SOFA score, number of failing organs, and duration of ICU stay. The value of exacerbation frequency for predicting the outcome of COPD was excellent (AUC: 0.892), with a sensitivity of 0.851 and a specificity of 0.797.
Conclusions: The SOFA score, determined at the onset of MODS in elderly patients with COPD, was a reliable predictor of the prognosis. The exacerbation frequency, number of failing organs, and the SOFA score were risk factors of a poor prognosis, and the exacerbation frequency could also effectively predict the outcome of COPD.
Keywords: Acute exacerbation (AE); chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS); prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Establishment of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome early warning score in patients with severe trauma and its clinical significance: a multicenter study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Jan;30(1):41-46. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.01.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29308756 Chinese.
-
[Predictive values of different critical scoring systems for survival rate after discharge in critically ill patients supported by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 May;30(5):456-460. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.05.012. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29764551 Chinese.
-
[Comparison of simplified acute physiology score III and other scoring systems in prediction of 28-day prognosis in patients with severe sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Jun;27(6):454-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.06.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26049183 Chinese.
-
[Comparison of three different organ failure assessment score systems in predicting outcome of severe sepsis].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Jan 1;47(1):48-50. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19484951 Chinese.
-
[Predictive value of four different scoring systems for septic patient's outcome: a retrospective analysis with 311 patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Feb;29(2):133-138. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.02.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 28625260 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Scores and Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in Invasive Aspergillosis from an Indian Respiratory Medicine ICU (ICU Patients with IA Suspicion).J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Nov 20;7(11):991. doi: 10.3390/jof7110991. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829278 Free PMC article.
-
SOFA score is superior to APACHE-II score in predicting the prognosis of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy.Ren Fail. 2020 Nov;42(1):638-645. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1788581. Ren Fail. 2020. PMID: 32660294 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Lactic Dehydrogenase-to-Albumin Ratio and Short-Time Mortality in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025 Jul 15;20:2435-2444. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S521192. eCollection 2025. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025. PMID: 40688237 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of the CURB-65, qSOFA, and APACHE II for in-hospital mortality in patients with acute exacerbation chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 11;103(41):e40022. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040022. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465785 Free PMC article.
-
To develop a regional ICU mortality prediction model during the first 24 h of ICU admission utilizing MODS and NEMS with six other independent variables from the Critical Care Information System (CCIS) Ontario, Canada.J Intensive Care. 2016 Feb 29;4:16. doi: 10.1186/s40560-016-0143-6. eCollection 2016. J Intensive Care. 2016. PMID: 26933498 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
