Aerobic Exercise Training Prevents the Onset of Endothelial Dysfunction via Increased Nitric Oxide Bioavailability and Reduced Reactive Oxygen Species in an Experimental Model of Menopause
- PMID: 25923465
- PMCID: PMC4414603
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125388
Aerobic Exercise Training Prevents the Onset of Endothelial Dysfunction via Increased Nitric Oxide Bioavailability and Reduced Reactive Oxygen Species in an Experimental Model of Menopause
Abstract
Objective: Previous studies have shown that estrogen deficiency, arising in postmenopause, promotes endothelial dysfunction. This study evaluated the effects of aerobic exercise training on endothelial dependent vasodilation of aorta in ovariectomized rats, specifically investigating the role of nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Methods: Female Wistar rats ovariectomized (OVX - n=20) or with intact ovary (SHAM - n=20) remained sedentary (OVX and SHAM) or performed aerobic exercise training on a treadmill 5 times a week for a period of 8 weeks (OVX-TRA and SHAM-TRA). In the thoracic aorta the endothelium-dependent and -independent vasodilation was assessed by acetylcholine (ACh) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP), respectively. Certain aortic rings were incubated with L-NAME to assess the NO modulation on the ACh-induced vasodilation. The fluorescence to dihydroethidium in aortic slices and plasma nitrite/nitrate concentrations were measured to evaluate ROS and NO bioavailability, respectively.
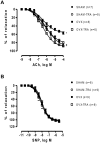
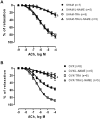
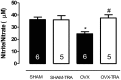
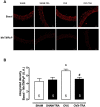
Results: ACh-induced vasodilation was reduced in OVX rats as compared SHAM (Rmax: SHAM: 86±3.3 vs. OVX: 57±3.0%, p<0.01). Training prevented this response in OVX-TRA (Rmax: OVX-TRA: 88±2.0%, p<0.01), while did not change it in SHAM-TRA (Rmax: SHAM-TRA: 80±2.2%, p<0.01). The L-NAME incubation abolished the differences in ACh-induced relaxation among groups. SNP-induced vasodilation was not different among groups. OVX reduced nitrite/nitrate plasma concentrations and increased ROS in aortic slices, training as effective to restore these parameters to the SHAM levels.
Conclusions: Exercise training, even in estrogen deficiency conditions, is able to improve endothelial dependent vasodilation in rat aorta via enhanced NO bioavailability and reduced ROS levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- VI Diretrizes Brasileira de Hipertensão. Revista Brasileira de Hipertensão. 2010;13(1):6–66.
-
- Lejskova M, Alusik S, Valenta Z, Adamkova S, Pitha J. Natural postmenopause is associated with an increase in combined cardiovascular risk factors. Physiol Res. 2012;61(6):587–96. Epub 2012/10/27. . - PubMed
-
- Ito K, Hirooka Y, Kimura Y, Sagara Y, Sunagawa K. Ovariectomy Augments Hypertension Through Rho-Kinase Activation in the Brain Stem in Female Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension. 2006;48:651 a 7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

