Tidal volume estimation using the blanket fractal dimension of the tracheal sounds acquired by smartphone
- PMID: 25923929
- PMCID: PMC4481932
- DOI: 10.3390/s150509773
Tidal volume estimation using the blanket fractal dimension of the tracheal sounds acquired by smartphone
Abstract
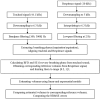
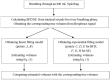
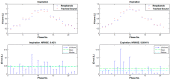
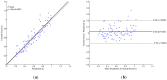
In this paper, we propose the use of blanket fractal dimension (BFD) to estimate the tidal volume from smartphone-acquired tracheal sounds. We collected tracheal sounds with a Samsung Galaxy S4 smartphone, from five (N = 5) healthy volunteers. Each volunteer performed the experiment six times; first to obtain linear and exponential fitting models, and then to fit new data onto the existing models. Thus, the total number of recordings was 30. The estimated volumes were compared to the true values, obtained with a Respitrace system, which was considered as a reference. Since Shannon entropy (SE) is frequently used as a feature in tracheal sound analyses, we estimated the tidal volume from the same sounds by using SE as well. The evaluation of the performed estimation, using BFD and SE methods, was quantified by the normalized root-mean-squared error (NRMSE). The results show that the BFD outperformed the SE (at least twice smaller NRMSE was obtained). The smallest NRMSE error of 15.877% ± 9.246% (mean ± standard deviation) was obtained with the BFD and exponential model. In addition, it was shown that the fitting curves calculated during the first day of experiments could be successfully used for at least the five following days.
Figures




References
-
- Sovijarvi A.R.A., Dalmasso F., Vanderschoot J., Malmberg L.P., Righini G., Stoneman S.A.T. Definition of terms for applications of respiratory sounds. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2000;10:597–610.
-
- Moussavi Z. Fundamentals of Respiratory Sounds and Analysis. 1st ed. Morgan & Claypool Publishers; San Rafael, CA, USA: 2006.
-
- Sovijarvi A.R.A., Malmberg L.P., Charbonneau G., Vanderschoot J., Dalmasso F., Sacco C., Rossi M., Earis J.E. Characteristics of breath sounds and adventitious respiratory sounds. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2000;10:591–596.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

