Analysis of the interrelationship of the pulmonary irritation and elicitation thresholds in rats sensitized with 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI)
- PMID: 25924102
- PMCID: PMC4496806
- DOI: 10.3109/08958378.2015.1026619
Analysis of the interrelationship of the pulmonary irritation and elicitation thresholds in rats sensitized with 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI)
Abstract
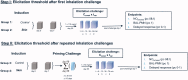
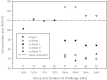
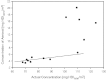
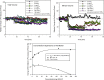
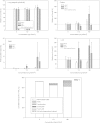
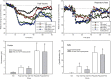
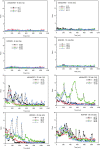
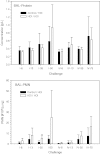
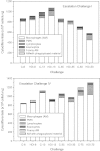
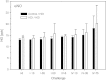
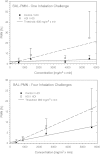
This paper summarizes a range of experimental data central for developing a science-based approach for hazard identification of monomeric and polymeric aliphatic 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI). The dose-response curve of HDI-induced pulmonary responses in naïve or dermally sensitized rats after one or several inhalation priming exposures was examined in the Brown Norway (BN) rat asthma model. Emphasis was directed to demonstrate the need and the difficulty in selecting an appropriate pulmonary dose when much of the inhaled chemically reactive vapor may concentration dependently be retained in the upper airways of obligate nose-breathing rats. The course taken acknowledges the experimental challenges in identifying an elicitation threshold for HDI-monomer near or above the saturated vapor concentration or in the presence of a HDI-polymer aerosol. The inhalation threshold dose on elicitation was determined based on a fixed concentration (C) × variable exposure duration (t) protocol for improving inhalation dosimetry of the lower airways. Neutrophilic granulocytes (PMN) in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid in equally inhalation primed naïve and dermally sensitized rats were used to define the inhalation elicitation threshold C × t. Sensitized rats elaborated markedly increased PMN challenged sensitized rats relative to equally challenged naïve rats at 5625 mg HDI/m(3) × min (75 mg/m(3) for 75 min). PMN were essentially indistinguishable at 900 mg HDI/m(3) × min. By applying adjustment factors accounting for both inter-species differences in inhalation dosimetry and intra-species susceptibility, the workplace human-equivalent threshold C × t was estimated to be in the range of the current ACGIH TLV® of HDI. Thus, this rat "asthma" model was suitable to demonstrate elicitation thresholds for HDI-vapor after one or several inhalation priming exposures and seems to be suitable to derive occupational exposure values (OELs) for diisocyanates in general.
Keywords: Asthma rat bioassay; diisocyanate asthma; dose–response; neutrophilic inflammation; risk assessment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of a respiratory sensitization/elicitation protocol of toluene diisocyanate (TDI) in Brown Norway rats to derive an elicitation-based occupational exposure level.Toxicology. 2014 May 7;319:10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Feb 23. Toxicology. 2014. PMID: 24572447
-
Brown Norway rat asthma model of diphenylmethane-4,4'-diisocyanate (MDI): determination of the elicitation threshold concentration of after inhalation sensitization.Toxicology. 2011 Mar 15;281(1-3):15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2011.01.005. Epub 2011 Jan 13. Toxicology. 2011. PMID: 21237241
-
Brown Norway rat asthma model of diphenylmethane-4,4'-diisocyanate (MDI): analysis of the elicitation dose-response relationship.Toxicol Sci. 2008 Aug;104(2):320-31. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfn098. Epub 2008 May 20. Toxicol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18495671
-
Thresholds in chemical respiratory sensitisation.Toxicology. 2015 Jul 3;333:179-194. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2015.04.010. Epub 2015 May 8. Toxicology. 2015. PMID: 25963507 Review.
-
Acute inhalation studies with irritant aerosols: technical issues and relevance for risk characterization.Arch Toxicol. 2004 May;78(5):243-51. doi: 10.1007/s00204-003-0516-1. Epub 2004 Apr 1. Arch Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 15057506 Review.
References
-
- Aalto-Korte K, Suuronen K, Kuuliala O, et al. Occupational contact allergy to monomeric isocyanates. Contact Dermatitis. 2011;67:78–88. - PubMed
-
- Alexandersson R, Hedenstierna G, Plato N, Kolmodin-Hedman B. Exposure, lung function, and symptoms in car painters exposed to hexamethylene diisocyanate and biuret modified hexamethylene diisocyanate. Arch Environ Health. 1987;42:367–73. - PubMed
-
- Arts JH, de Jong WH, van Triel JJ, et al. The respiratory local lymph node assay as a tool to study respiratory sensitizers. Toxicol Sci. 2008;106:423–34. - PubMed
-
- Baur X. Evidence for allergic reactions in isocyanate asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:757–8. - PubMed
-
- Baur X, Marek W, Ammon J, et al. Respiratory and other hazards of isocyanates. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1994;66:141–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
