Intracranial trigeminal schwannoma
- PMID: 25924170
- PMCID: PMC4757116
- DOI: 10.15274/NRJ-2014-10117
Intracranial trigeminal schwannoma
Abstract
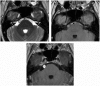
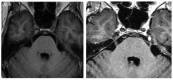
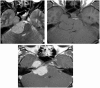
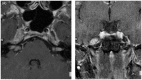
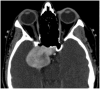
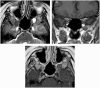
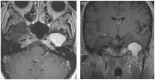
Intracranial trigeminal schwannomas are rare tumors. Patients usually present with symptoms of trigeminal nerve dysfunction, the most common symptom being facial pain. MRI is the imaging modality of choice and is usually diagnostic in the appropriate clinical setting. The thin T2-weighted CISS 3D axial sequence is important for proper assessment of the cisternal segment of the nerve. They are usually hypointense on T1, hyperintense on T2 with avid enhancement post gadolinium. CT scan is supplementary to MRI, particularly for tumors located in the skull base. Imaging plays a role in diagnosis and surgical planning. In this pictorial essay, we retrospectively reviewed imaging findings in nine patients with pathologically proven trigeminal schwannoma. Familiarity with the imaging findings of intracranial trigeminal schwannoma may help to diagnose this entity.
Keywords: MR; schwannoma; trigeminal nerve.
© The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions:sagepub.co.uk/journalsPermissions.nav.
Figures


References
-
- Arseni C, Dumitrescu L, Constantinescu A. Neurinomas of the trigeminal nerve. Surg Neurol. 1975; 4(6): 497–503. - PubMed
-
- McCormick PC, Bello JA, Post KD. Trigeminal schwannoma. Surgical series of 14 cases with review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1988; 69(6): 850–860. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.69.6.0850. - PubMed
-
- Pollack IF, Sekhar LN, Jannetta PJ, et al. Neurilemomas of the trigeminal nerve. J Neurosurg. 1989; 70(5): 737–745. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.70.5.0737. - PubMed
-
- Borges A, Casselman J. Imaging the trigeminal nerve. Eur J Radiol. 2010; 74(2): 323–340. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.02.006. - PubMed
-
- Bathla G, Hegde AN. The trigeminal nerve: an illustrated review of its imaging anatomy and pathology. Clin Radiol. 2013; 68(2): 203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2012.05.019. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

