Epinephrine reversed high-concentration bupivacaine-induced inhibition of calcium channels and transient outward potassium current channels, but not on sodium channel in ventricular myocytes of rats
- PMID: 25924894
- PMCID: PMC4422592
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-015-0049-1
Epinephrine reversed high-concentration bupivacaine-induced inhibition of calcium channels and transient outward potassium current channels, but not on sodium channel in ventricular myocytes of rats
Abstract
Background: Epinephrine is a first-line drug for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, but its efficacy in the treatment of bupivacaine-induced cardiac toxicity is still in question. We hypothesized that epinephrine can reverse cardiac inhibition of bupivacaine by modulating ion flows through the ventricular myocyte membrane channels of rats. The aim of this study was to observe and report the effects of epinephrine on high-concentration bupivacaine-induced inhibition of sodium (INa), L-type calcium (ICa-L), and transient outward potassium (Ito) currents in the ventricular myocytes of rats.
Methods: The ventricular myocytes were isolated from Sprague-Dawley rats (250-300 g) by acute enzymatic dissociation. The whole-cell patch clamp technique was used to record the ion channel currents in single ventricular myocytes both before and after administration of medications.
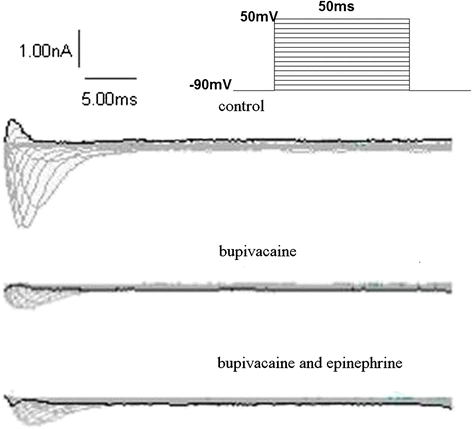
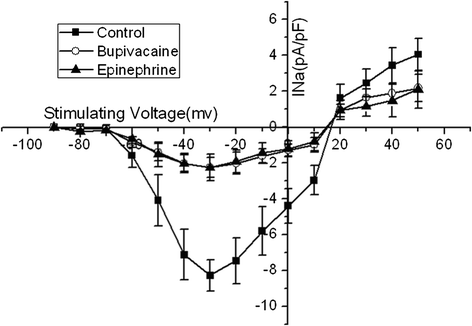
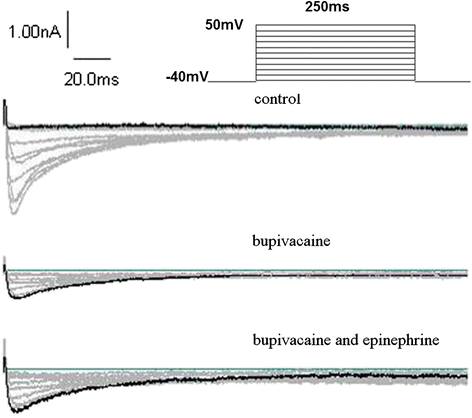
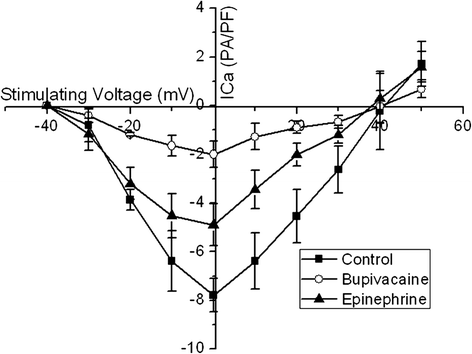
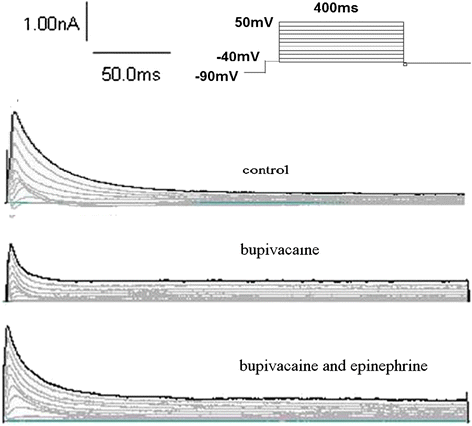
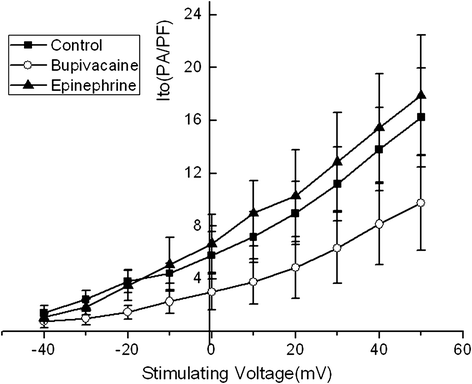
Result: Administration of bupivacaine 100 μmol/L significantly reduced INa, (P < 0.05). However, administration of bupivacaine 100 μmol/L in conjunction with epinephrine 0.15 μg/ml had no effect in restoring INa to its previous state. Similarly, a sharp decline of ICa-L and Ito was observed after administration of bupivacaine 100 μmol/L (P < 0.05). In contrast to INa, ICa-L and Ito were significantly improved after the administration of the aforementioned combination of bupivacaine and epinephrine (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Epinephrine can reverse high-concentration bupivacaine induced inhibition of ICa-L and Ito, but not INa. Thus, epinephrine's effectiveness in reversal of bupivacaine-induced cardiac toxicity secondary to sodium channel inhibition may be limited.
Figures
References
-
- Heavner JE, Pitkanen MT, Shi B, Rosenberg PH. Resuscitation from bupivacaine-induced asystole in rats: comparison of different cardioactive drugs. Anesth Analg. 1995;80(6):1134–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

