Muc1 is protective during kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 25925251
- PMCID: PMC4469889
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00066.2015
Muc1 is protective during kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
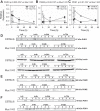
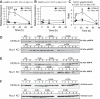
Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) due to hypotension is a common cause of human acute kidney injury (AKI). Hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs) orchestrate a protective response in renal endothelial and epithelial cells in AKI models. As human mucin 1 (MUC1) is induced by hypoxia and enhances HIF-1 activity in cultured epithelial cells, we asked whether mouse mucin 1 (Muc1) regulates HIF-1 activity in kidney tissue during IRI. Whereas Muc1 was localized on the apical surface of the thick ascending limb, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct in the kidneys of sham-treated mice, Muc1 appeared in the cytoplasm and nucleus of all tubular epithelia during IRI. Muc1 was induced during IRI, and Muc1 transcripts and protein were also present in recovering proximal tubule cells. Kidney damage was worse and recovery was blocked during IRI in Muc1 knockout mice compared with congenic control mice. Muc1 knockout mice had reduced levels of HIF-1α, reduced or aberrant induction of HIF-1 target genes involved in the shift of glucose metabolism to glycolysis, and prolonged activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, indicating metabolic stress. Muc1 clearly plays a significant role in enhancing the HIF protective pathway during ischemic insult and recovery in kidney epithelia, providing a new target for developing therapies to treat AKI. Moreover, our data support a role specifically for HIF-1 in epithelial protection of the kidney during IRI as Muc1 is present only in tubule epithelial cells.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; Muc1; acute kidney injury; hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1); ischemia.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures






References
-
- Adkison D, Hollwarth ME, Benoit JN, Parks DA, McCord JM, Granger DN. Role of free radicals in ischemia-reperfusion injury to the liver. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 548: 101–107, 1986. - PubMed
-
- Aubert S, Fauquette V, Hemon B, Lepoivre R, Briez N, Bernard D, Van Seuningen I, Leroy X, Perrais M. MUC1, a new hypoxia inducible factor target gene, is an actor in clear renal cell carcinoma tumor progression. Cancer Res 69: 5707–5715, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt WM, Campean V, Kany S, Jurgensen JS, Weidemann A, Warnecke C, Arend M, Klaus S, Gunzler V, Amann K, Willam C, Wiesener MS, Eckardt KU. Preconditional activation of hypoxia-inducible factors ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1970–1978, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Bleyer AJ, Kmoch S, Antignac C, Robins V, Kidd K, Kelsoe JR, Hladik G, Klemmer P, Knohl SJ, Scheinman SJ, Vo N, Santi A, Harris A, Canaday O, Weller N, Hulick PJ, Vogel K, Rahbari-Oskoui FF, Tuazon J, Deltas C, Somers D, Megarbane A, Kimmel PL, Sperati CJ, Orr-Urtreger A, Ben-Shachar S, Waugh DA, McGinn S, Bleyer AJ Jr, Hodanova K, Vylet'al P, Zivna M, Hart TC, Hart PS. Variable clinical presentation of an MUC1 mutation causing medullary cystic kidney disease type 1. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9: 527–535, 2014. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braga VM, Pemberton LF, Duhig T, Gendler SJ. Spatial and temporal expression of an epithelial mucin, Muc-1, during mouse development. Development 115: 427–437, 1992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK080821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-077124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-62277/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK097889/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA-64389/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-080821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-100287/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-097889/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-103776/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK077124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-081646/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-095498/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-084184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-075048/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081646/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075048/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002348/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- DK-099345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-101791/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101791/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

