Phase II Trial of Preoperative Radiation With Concurrent Capecitabine, Oxaliplatin, and Bevacizumab Followed by Surgery and Postoperative 5-Fluorouracil, Leucovorin, Oxaliplatin (FOLFOX), and Bevacizumab in Patients With Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: 5-Year Clinical Outcomes ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group E3204
- PMID: 25926352
- PMCID: PMC4571787
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0106
Phase II Trial of Preoperative Radiation With Concurrent Capecitabine, Oxaliplatin, and Bevacizumab Followed by Surgery and Postoperative 5-Fluorouracil, Leucovorin, Oxaliplatin (FOLFOX), and Bevacizumab in Patients With Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: 5-Year Clinical Outcomes ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group E3204
Abstract
Lessons learned: The 5-year oncologic outcomes from the trial regimen were excellent. However, the neoadjuvant and surgical toxicity of this regimen was significant and was the primary reason for the low compliance with adjuvant systemic therapy.Due to the lack of an improvement in the pathologic complete response rate, the substantial associated toxicity, and the negative phase III trials of adjuvant bevacizumab in colon cancer, this regimen will not be pursued for further study.
Background: The addition of bevacizumab to chemotherapy improves overall survival for metastatic colorectal cancer. We initiated a phase II trial to evaluate preoperative capecitabine, oxaliplatin, and bevacizumab with radiation therapy (RT) followed by surgery and postoperative 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin (FOLFOX), and bevacizumab for locally advanced rectal cancer. The purpose of this report is to describe the 5-year oncologic outcomes of this regimen.
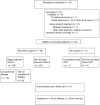
Methods: In a phase II Simon two-stage design study, we evaluated preoperative treatment with capecitabine (825 mg/m(2) b.i.d. Monday-Friday), oxaliplatin (50 mg/m(2) weekly), bevacizumab (5 mg/kg on days 1, 15, and 29), and RT (50.4 Gy). Surgery was performed by 8 weeks after RT. Beginning 8-12 weeks after surgery, patients received FOLFOX plus bevacizumab (5 mg/kg) every 2 weeks for 12 cycles (oxaliplatin stopped after 9 cycles). The primary endpoint was a pathologic complete response (path-CR) rate of 30%. Fifty-seven patients with resectable T3/T4 rectal adenocarcinoma were enrolled between 2006 and 2010.
Results: Of 57 enrolled patients, 53 were eligible and included in the analysis. Forty-eight (91%) patients completed preoperative therapy, all of whom underwent curative surgical resection. Nine patients (17%) achieved path-CR. There were 29 worst grade 3 events, 8 worst grade 4 events, and 2 patient deaths, 1 of which was attributed to study therapy. Twenty-six patients (54%) began adjuvant chemotherapy. After a median follow-up period of 41 months, the 5-year overall survival (OS) rate for all patients was 80%. Only 2 patients experienced cancer recurrence: 1 distant (liver) and 1 loco-regional (pelvic lymph nodes), respectively. Both of these patients are still alive. The 5-year relapse-free survival rate was 81%.
Conclusion: Despite the path-CR primary endpoint of this trial not being reached, the 5-year OS and recurrence-free survival rates were excellent. However, the neoadjuvant and surgical toxicity of this regimen was significant and was the primary reason for the low compliance with adjuvant systemic therapy. Because of the lack of an improvement in the path-CR rate, the substantial associated toxicity, and the negative phase III trials of adjuvant bevacizumab in colon cancer, this regimen will not be pursued for further study.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00321685.
©AlphaMed Press; the data published online to support this summary is the property of the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase 2 study of preoperative radiation with concurrent capecitabine, oxaliplatin, and bevacizumab followed by surgery and postoperative 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin (FOLFOX), and bevacizumab in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: ECOG 3204.Cancer. 2013 Apr 15;119(8):1521-7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27890. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23288663 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin versus fluorouracil and leucovorin as adjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy (ADORE): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Oct;15(11):1245-53. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70377-8. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25201358 Clinical Trial.
-
Oxaliplatin added to fluorouracil-based preoperative chemoradiotherapy and postoperative chemotherapy of locally advanced rectal cancer (the German CAO/ARO/AIO-04 study): final results of the multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2015 Aug;16(8):979-89. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00159-X. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Lancet Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26189067 Clinical Trial.
-
Current status of adjuvant therapy for colorectal cancer.Oncology (Williston Park). 2004 May;18(6):751-5; discussion 755-8. Oncology (Williston Park). 2004. PMID: 15214594 Review.
-
The role of capecitabine in locally advanced rectal cancer treatment: an update.Drugs. 2012 May 28;72(8):1057-73. doi: 10.2165/11633870-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22621694 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic review of treatment intensification using novel agents for chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer.Br J Surg. 2018 Nov;105(12):1553-1572. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10993. Br J Surg. 2018. PMID: 30311641 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I Study of Lenvatinib and Capecitabine with External Radiation Therapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Adenocarcinoma.Oncologist. 2022 Aug 5;27(8):621-e617. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyac003. Oncologist. 2022. PMID: 35325225 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The clinical application of angiostatic therapy in combination with radiotherapy: past, present, future.Angiogenesis. 2017 May;20(2):217-232. doi: 10.1007/s10456-017-9546-9. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Angiogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28364160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and safety of adding bevacizumab in neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced rectal cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Oncol. 2021 Jan;14(1):100964. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100964. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33248411 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule inhibitors, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and more: FDA-approved novel therapeutic drugs for solid tumors from 1991 to 2021.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Oct 8;15(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01362-9. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36209184 Free PMC article. Review.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical