Neuropeptide receptor transcript expression levels and magnitude of ionic current responses show cell type-specific differences in a small motor circuit
- PMID: 25926455
- PMCID: PMC4412897
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0171-15.2015
Neuropeptide receptor transcript expression levels and magnitude of ionic current responses show cell type-specific differences in a small motor circuit
Abstract
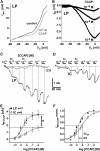
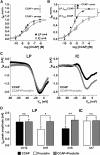
We studied the relationship between neuropeptide receptor transcript expression and current responses in the stomatogastric ganglion (STG) of the crab, Cancer borealis. We identified a transcript with high sequence similarity to crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) receptors in insects and mammalian neuropeptide S receptors. This transcript was expressed throughout the nervous system, consistent with the role of CCAP in a range of different behaviors. In the STG, single-cell qPCR showed expression in only a subset of neurons. This subset had previously been shown to respond to CCAP with the activation of a modulator-activated inward current (IMI), with one exception. In the one cell type that showed expression but no IMI responses, we found CCAP modulation of synaptic currents. Expression levels within STG neuron types were fairly variable, but significantly different between some neuron types. We tested the magnitude and concentration dependence of IMI responses to CCAP application in two identified neurons, the lateral pyloric (LP) and the inferior cardiac (IC) neurons. LP had several-fold higher expression and showed larger current responses. It also was more sensitive to low CCAP concentrations and showed saturation at lower concentrations, as sigmoid fits showed smaller EC50 values and steeper slopes. In addition, occlusion experiments with proctolin, a different neuropeptide converging onto IMI, showed that saturating concentrations of CCAP activated all available IMI in LP, but only approximately two-thirds in IC, the neuron with lower receptor transcript expression. The implications of these findings for comodulation are discussed.
Keywords: crustacean cardioactive peptide; neuromodulation; proctolin; stomatogastric.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/356786-15$15.00/0.
Figures




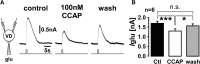
Similar articles
-
Graded Transmission without Action Potentials Sustains Rhythmic Activity in Some But Not All Modulators That Activate the Same Current.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 17;38(42):8976-8988. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2632-17.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30185461 Free PMC article.
-
Modulators with convergent cellular actions elicit distinct circuit outputs.J Neurosci. 2001 Jun 1;21(11):4050-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-11-04050.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11356892 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of endogenous neuromodulators in a small motor network enhances responsiveness to neuromodulation.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Sep 1;118(3):1749-1761. doi: 10.1152/jn.00383.2017. Epub 2017 Jun 28. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28659465 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of stomatogastric rhythms.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2009 Nov;195(11):989-1009. doi: 10.1007/s00359-009-0483-y. Epub 2009 Oct 11. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19823843 Review.
-
Neuropeptide modulation of microcircuits.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012 Aug;22(4):592-601. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2012.01.003. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22305485 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The complexity of small circuits: the stomatogastric nervous system.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016 Dec;41:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27450880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graded Transmission without Action Potentials Sustains Rhythmic Activity in Some But Not All Modulators That Activate the Same Current.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 17;38(42):8976-8988. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2632-17.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30185461 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping circuit dynamics during function and dysfunction.Elife. 2022 Mar 18;11:e76579. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76579. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35302489 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide modulation of pattern-generating systems in crustaceans: comparative studies and approaches.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016 Dec;41:149-157. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27693928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feeding state-dependent modulation of feeding-related motor patterns.J Neurophysiol. 2021 Dec 1;126(6):1903-1924. doi: 10.1152/jn.00387.2021. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 34669505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arakane Y, Li B, Muthukrishnan S, Beeman RW, Kramer KJ, Park Y. Functional analysis of four neuropeptides, EH, ETH, CCAP and bursicon, and their receptors in adult ecdysis behavior of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Mech Dev. 2008;125:984–995. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.09.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
