Angiotensin(1-7) and ACE2, "The Hot Spots" of Renin-Angiotensin System, Detected in the Human Aqueous Humor
- PMID: 25926900
- PMCID: PMC4407001
- DOI: 10.2174/1874364101509010028
Angiotensin(1-7) and ACE2, "The Hot Spots" of Renin-Angiotensin System, Detected in the Human Aqueous Humor
Abstract
Background: The main purpose of the study was to establish whether essential components of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) exist in the human aqueous humor.
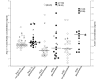
Methods: Forty-five patients ≥ 60 (74±7) years of age undergoing cataract surgery at Tampere University Hospital were randomly selected for the prospective study. The exclusion criterion was the use of oral antihypertensive medicine acting via renin-angiotensin system. Aqueous humor samples were taken at the beginning of normal cataract extraction. The samples were frozen and stored at -80 °C. The concentrations of intraocular endogenous RAS components Ang(1-7), ACE2, and ACE1 were measured using ELISA.
Results: Concentration medians of Ang(1-7), ACE2, and ACE1 in the aqueous humor were: Ang(1-7) 4.08 ng/ml, ACE2 2.32 ng/ml and ACE1 0.35 ng/ml. The concentrations were significantly higher in glaucomatous than in non-glaucomatous eyes, ACE1 (p=0.014) and Ang(1-7) (p=0.026) vs non-glaucomatous eyes.
Conclusions: Ang(1-7), ACE2 and ACE1 are found in the human aqueous humor. The observations are consistent with the conception that local tissue-RAS exists in the human eye and it might have a role in the control of intraocular pressure.
Keywords: Angiotensin (1-7); angiotensin II; angiotensin converting enzyme 1; angiotensin converting enzyme 2; aqueous humor; glaucoma; renin-angiotensin system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Many Faces of Renin-angiotensin System - Focus on Eye.Open Ophthalmol J. 2017 Jun 19;11:122-142. doi: 10.2174/1874364101711010122. eCollection 2017. Open Ophthalmol J. 2017. PMID: 28761566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local ocular renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: any connection with intraocular pressure? A comprehensive review.Ann Med. 2020 Aug;52(5):191-206. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1758341. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Ann Med. 2020. PMID: 32308046 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous humor renin, angiotensin I, and angiotensin II activity in primary open-angle glaucoma.Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2020 Aug;83(4):318-322. doi: 10.5935/0004-2749.20200052. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2020. PMID: 32756783 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in BeWo and HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cell lines.Placenta. 2012 Aug;33(8):634-9. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2012.05.001. Epub 2012 May 28. Placenta. 2012. PMID: 22647832
-
ACE and ACE2 in kidney disease.World J Nephrol. 2015 Feb 6;4(1):74-82. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i1.74. World J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25664248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The eye: "An organ that must not be forgotten in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-2019) pandemic".J Optom. 2021 Apr-Jun;14(2):114-119. doi: 10.1016/j.optom.2020.07.002. Epub 2020 Jul 15. J Optom. 2021. PMID: 32763128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular Manifestations of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Comprehensive Review.J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2021 Apr 29;16(2):234-247. doi: 10.18502/jovr.v16i2.9087. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2021. PMID: 34055261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Danish Nationwide Data Reveal a Link between Diabetes Mellitus, Diabetic Retinopathy, and Glaucoma.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:2684674. doi: 10.1155/2016/2684674. Epub 2016 Oct 31. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 27872861 Free PMC article.
-
Personal Protective Equipment and COVID-19: A Review for Surgeons.Ann Surg. 2020 Aug;272(2):e132-e138. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003991. Ann Surg. 2020. PMID: 32675516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular neuroinflammatory response secondary to SARS-CoV-2 infection-a review.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 4;16:1515768. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1515768. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39967658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paul M, Poyan Mehr A, Kreutz R. Physiology of local renin angiotensin systems. Rev Physiol Rev. 2006;86:747–803. - PubMed
-
- Kramkowski K, Mogielnicki A, Buczko W. The physiological significance of the alternative pathways of angiotensin II production. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;57:529–39. - PubMed
-
- Danser AHJ, Derkx FHM, Admiraal PJJ , et al. Angiotensin levels in the eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35:1008–18. - PubMed
-
- Savaskan E, Loffler KU, Meier F , et al. Immunohistochemical localization of angiotensin-converting enzyme, angiotensin II and AT1 receptor in human ocular tissues. Ophthalmic Res. 2004;36:312–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
