A novel mechanism of regulation of the anti-metastatic miR-31 by EMSY in breast cancer
- PMID: 25927669
- PMCID: PMC4429417
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-014-0467-x
A novel mechanism of regulation of the anti-metastatic miR-31 by EMSY in breast cancer
Abstract
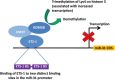
miR-31 is well known as an anti-metastatic microRNA (miRNA) in the context of breast cancer. However, to date the mechanism of regulation of this miRNA has yet to be elucidated. The recent publication by Viré et al. in Molecular Cell demonstrates for the first time that one mechanism of regulation of miR-31 is through the putative oncogene EMSY, whose amplification in breast cancer patients correlates with reduced expression of the miRNA. This regulation is dependent on the DNA-binding transcription factor ETS-1 which recruits EMSY and the histone demethylase KDM5B to the miR-31 promoter, thus repressing its transcription.
Figures
Comment on
-
The breast cancer oncogene EMSY represses transcription of antimetastatic microRNA miR-31.Mol Cell. 2014 Mar 6;53(5):806-18. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.01.029. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24582497 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous