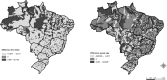
Impact of income inequality and other social determinants on suicide rate in Brazil
- PMID: 25928359
- PMCID: PMC4416030
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124934
Impact of income inequality and other social determinants on suicide rate in Brazil
Abstract
Purpose: To analyze whether income inequality and other social determinants are associated with suicide rate in Brazil.
Method: This study used panel data from all 5,507 Brazilian municipalities from 2000 to 2011. Suicide rates were calculated by sex and standardized by age for each municipality and year. The independent variables of the regression model included the Gini Index, per capita income, percentage of individuals with up to eight years of education, urbanization, average number of residents per household, percentage of divorced people, of Catholics, Pentecostals, and Evangelicals. A multivariable negative binomial regression for panel data with fixed-effects specification was performed.
Results: The Gini index was positively associated with suicide rates; the rate ratio (RR) was 1.055 (95% CI: 1.011-1.101). Of the other social determinants, income had a significant negative association with suicide rates (RR: 0.968, 95% CI: 0.948-0.988), whereas a low-level education had a positive association (RR: 1.015, 95% CI: 1.010-1.021).
Conclusions: Income inequality represents a community-level risk factor for suicide rates in Brazil. The decrease in income inequality, increase in income per capita, and decrease in the percentage of individuals who did not complete basic studies may have counteracted the increase in suicides in the last decade. Other changes, such as the decrease in the mean residents per household, may have contributed to their increase. Therefore, the implementation of social policies that may improve the population's socioeconomic conditions and reduce income inequality in Brazil, and in other low and middle-income countries, can help to reduce suicide rates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- WHO, Suicide Prevention and special programs. Available: http://www.who.int/mental_health/prevention/suicide/suicideprevent/en/. Accessed 10 November 2013.
-
- de Mello-Santos C, Bertolote JM, Wang Y-P. Epidemiology of suicide in Brazil (1980–2000): characterization of age and gender rates of suicide. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 2005; 27:131–134 - PubMed
-
- Prevenção do suicídio: manual dirigido a profissionais das equipes de saúde mental, Ministério da Saúde, 2005. Available: http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/manual_editoracao.pdf. Accessed 3 June 2013.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical