Pharmacokinetic Drug Interaction Studies with Enzalutamide
- PMID: 25929560
- PMCID: PMC4580724
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-015-0283-1
Pharmacokinetic Drug Interaction Studies with Enzalutamide
Abstract
Background and objectives: Two phase I drug interaction studies were performed with oral enzalutamide, which is approved for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
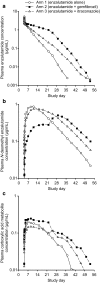
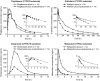
Methods: A parallel-treatment design (n = 41) was used to evaluate the effects of a strong cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 inhibitor (oral gemfibrozil 600 mg twice daily) or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (oral itraconazole 200 mg once daily) on the pharmacokinetics of enzalutamide and its active metabolite N-desmethyl enzalutamide after a single dose of enzalutamide (160 mg). A single-sequence crossover design (n = 14) was used to determine the effects of enzalutamide 160 mg/day on the pharmacokinetics of a single oral dose of sensitive substrates for CYP2C8 (pioglitazone 30 mg), CYP2C9 (warfarin 10 mg), CYP2C19 (omeprazole 20 mg), or CYP3A4 (midazolam 2 mg).
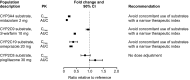
Results: Coadministration of gemfibrozil increased the composite area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity (AUC∞) of enzalutamide plus active metabolite by 2.2-fold, and coadministration of itraconazole increased the composite AUC∞ by 1.3-fold. Enzalutamide did not affect exposure to oral pioglitazone. Enzalutamide reduced the AUC∞ of oral S-warfarin, omeprazole, and midazolam by 56, 70, and 86 %, respectively; therefore, enzalutamide is a moderate inducer of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 and a strong inducer of CYP3A4.
Conclusions: If a patient requires coadministration of a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor with enzalutamide, then the enzalutamide dose should be reduced to 80 mg/day. It is recommended to avoid concomitant use of enzalutamide with narrow therapeutic index drugs metabolized by CYP2C9, CYP2C19, or CYP3A4, as enzalutamide may decrease their exposure.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01911728 NCT01913379.
Figures

Comment in
-
Enzalutamide: A Step Towards Pharmacokinetic-Based Dosing in Men with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015 Oct;54(10):989-91. doi: 10.1007/s40262-015-0293-z. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015. PMID: 26077984 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Effects of Strong CYP2C8 or CYP3A Inhibition and CYP3A Induction on the Pharmacokinetics of Brigatinib, an Oral Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitor, in Healthy Volunteers.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2020 Feb;9(2):214-223. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.723. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2020. PMID: 31287236 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Unintentional combining enzalutamide with a moderate CYP2C8 inhibitor in a patient with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a case report.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022 Apr;89(4):539-542. doi: 10.1007/s00280-021-04379-y. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35059789
-
Evaluation of Safety and Clinically Relevant Drug-Drug Interactions with Tucatinib in Healthy Volunteers.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022 Oct;61(10):1417-1426. doi: 10.1007/s40262-022-01144-z. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022. PMID: 35931943 Free PMC article.
-
Enzalutamide: Understanding and Managing Drug Interactions to Improve Patient Safety and Drug Efficacy.Drug Saf. 2024 Jul;47(7):617-641. doi: 10.1007/s40264-024-01415-7. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Drug Saf. 2024. PMID: 38607520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of drug-drug interactions in prostate cancer treatment: Focus on abiraterone acetate/prednisone and enzalutamide.Cancer Treat Rev. 2017 Apr;55:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017. PMID: 28340451 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetic Aspects of the Two Novel Oral Drugs Used for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Abiraterone Acetate and Enzalutamide.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016 Nov;55(11):1369-1380. doi: 10.1007/s40262-016-0403-6. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2016. PMID: 27106175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying Drug Interactions between Enzalutamide and Complementary Alternative Medications in a Patient with Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Case Report.Can J Hosp Pharm. 2018 Jul-Aug;71(4):276-281. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30186002 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Drug-drug interactions with proton pump inhibitors in cancer patients: an underrecognized cause of treatment failure.ESMO Open. 2023 Feb;8(1):100880. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.100880. Epub 2023 Feb 8. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 36764092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing Metabolic Liabilities of Ralaniten To Enhance Novel Androgen Receptor Targeted Therapies.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019 Sep 26;2(6):453-467. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.9b00065. eCollection 2019 Dec 13. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2019. PMID: 32259077 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Cancer Patients: An Opinion Paper.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 24;14(5):1156. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051156. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Guidance for industry: bioanalytical method validation, 2001. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidanc.... Accessed 13 Feb 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

