Females have a blunted cardiovascular response to one year of intensive supervised endurance training
- PMID: 25930024
- PMCID: PMC6345209
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00092.2015
Females have a blunted cardiovascular response to one year of intensive supervised endurance training
Abstract
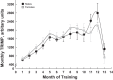
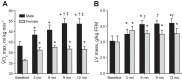
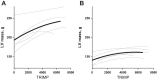
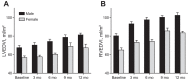
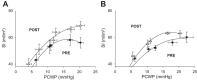
Cross-sectional studies in athletes suggest that endurance training augments cardiovascular structure and function with apparently different phenotypes in athletic males and females. It is unclear whether the longitudinal response to endurance training leads to similar cardiovascular adaptations between sexes. We sought to determine whether males and females demonstrate similar cardiovascular adaptations to 1 yr of endurance training, matched for training volume and intensity. Twelve previously sedentary males (26 ± 7, n = 7) and females (31 ± 6, n = 5) completed 1 yr of progressive endurance training. All participants underwent a battery of tests every 3 mo to determine maximal oxygen uptake (V̇o2max) and left ventricle (LV) function and morphology (cardiac magnetic resonance imaging). Pulmonary artery catheterization was performed before and after 1 yr of training, and pressure-volume and Starling curves were constructed during decreases (lower-body negative pressure) and increases (saline infusion) in cardiac volume. Males progressively increased V̇o2max, LV mass, and mean wall thickness, before reaching a plateau from month 9 to 12 of training. In contrast, despite exactly the same training, the response in females was markedly blunted, with V̇o2max, LV mass, and mean wall thickness plateauing after only 3 mo of training. The response of LV end-diastolic volume was not influenced by sex (males +20% and females +18%). After training Starling curves were shifted upward and left, but the effect was greatest in males (interaction P = 0.06). We demonstrate for the first time clear sex differences in response to 1 yr of matched endurance training, such that the development of ventricular hypertrophy and increase in V̇o2max in females is markedly blunted compared with males.
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; exercise training; gender.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Alway SE, Grumbt WH, Gonyea WJ, Stray-Gundersen J. Contrasts in muscle and myofibers of elite male and female bodybuilders. J Appl Physiol : 24–31, 1989. - PubMed
-
- American Dietetic Association, Dietitians of the American College of Sports Medicine, Rodriguez NR, Di Marco NM, Langley S. American College of Sports Medicine position stand Nutrition and athletic performance Med Sci Sports Exerc : 709–731, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Baggish AL, Wang F, Weiner RB, Elinoff JM, Tournoux F, Boland A, Picard MH, Hutter AM Jr, Wood MJ. Training-specific changes in cardiac structure and function: a prospective and longitudinal assessment of competitive athletes. J Appl Physiol : 1121–1128, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Banister EW, Morton RH, Fitz-Clarke J. Dose/response effects of exercise modeled from training: physical and biochemical measures. Ann Physiol Anthropol : 345–356, 1992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

