Kallistatin treatment attenuates lethality and organ injury in mouse models of established sepsis
- PMID: 25930108
- PMCID: PMC4445990
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-015-0919-4
Kallistatin treatment attenuates lethality and organ injury in mouse models of established sepsis
Abstract
Introduction: Kallistatin levels in the circulation are reduced in patients with sepsis and liver disease. Transgenic mice expressing kallistatin are resistant to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mortality. Here, we investigated the effect of kallistatin on survival and organ damage in mouse models of established sepsis.
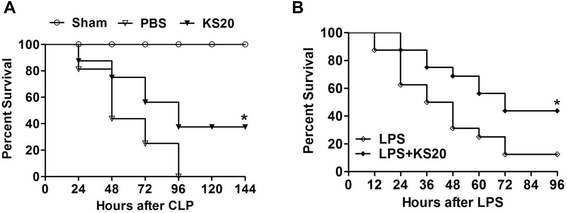
Methods: Mice were rendered septic by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), or endotoxemic by LPS injection. Recombinant human kallistatin was administered intravenously six hours after CLP, or intraperitoneally four hours after LPS challenge. The effect of kallistatin treatment on organ damage was examined one day after sepsis initiation, and mouse survival was monitored for four to six days.
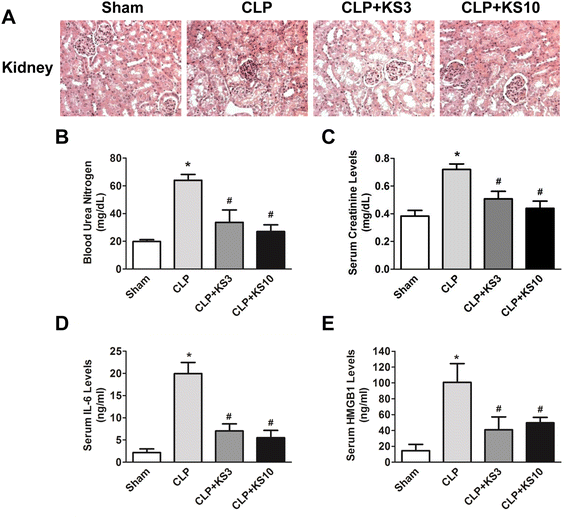
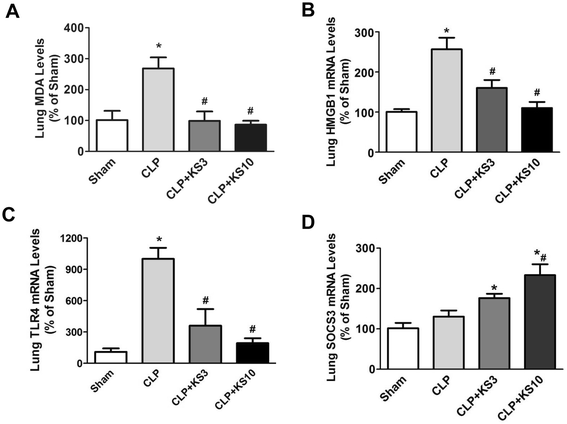
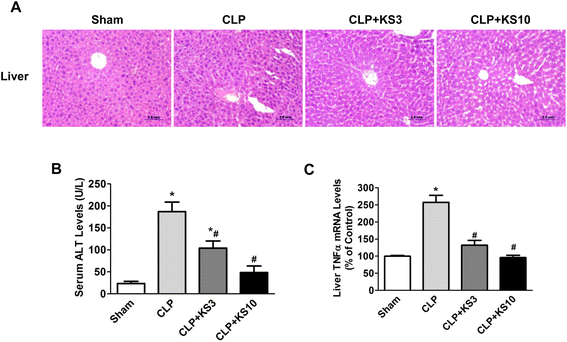
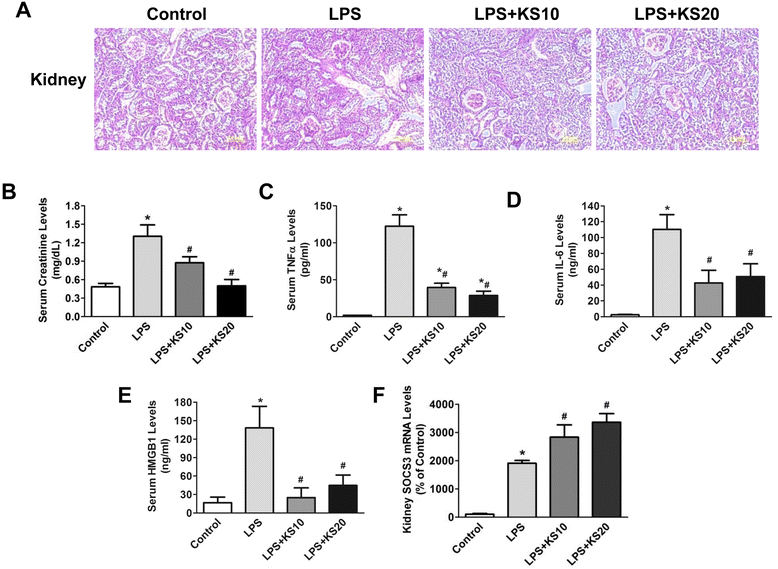
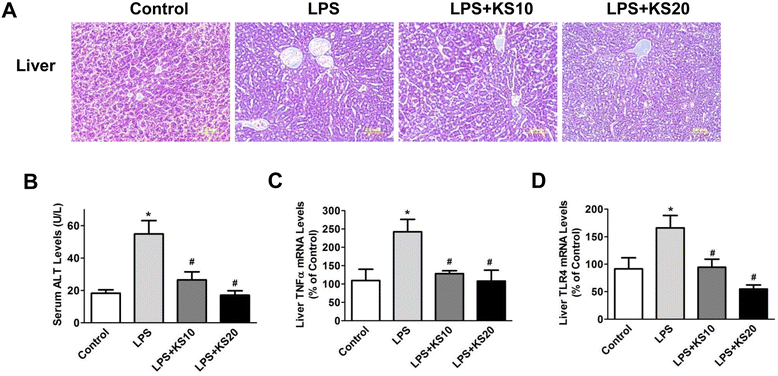
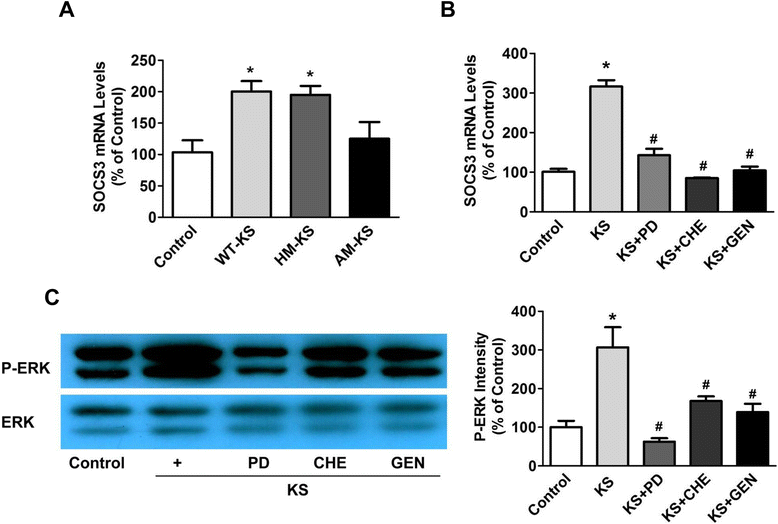
Results: Human kallistatin was detected in mouse serum of kallistatin-treated mice. Kallistatin significantly reduced CLP-induced renal injury as well as blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) levels. In the lung, kallistatin decreased malondialdehyde levels and HMGB1 and toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) synthesis, but increased suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS3) expression. Moreover, kallistatin attenuated liver injury, serum alanine transaminase (ALT) levels and hepatic tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) synthesis. Furthermore, delayed kallistatin administration improved survival in CLP mice by 38%, and LPS-treated mice by 42%. In LPS-induced endotoxemic mice, kallistatin attenuated kidney damage in association with reduced serum creatinine, IL-6 and HMGB1 levels, and increased renal SOCS3 expression. Kallistatin also decreased liver injury in conjunction with diminished serum ALT levels and hepatic TNF-α and TLR4 expression. In cultured macrophages, kallistatin through its active site increased SOCS3 expression, but this effect was blocked by inhibitors of tyrosine kinase, protein kinase C and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), indicating that kallistatin stimulates a tyrosine-kinase-protein kinase C-ERK signaling pathway.
Conclusions: This is the first study to demonstrate that delayed human kallistatin administration is effective in attenuating multi-organ injury, inflammation and mortality in mouse models of polymicrobial infection and endotoxemia. Thus, kallistatin therapy may provide a promising approach for the treatment of sepsis in humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Opposing Effects of Oxygen Regulation on Kallistatin Expression: Kallistatin as a Novel Mediator of Oxygen-Induced HIF-1-eNOS-NO Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5262958. doi: 10.1155/2017/5262958. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29387292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human kallistatin administration reduces organ injury and improves survival in a mouse model of polymicrobial sepsis.Immunology. 2014 Jun;142(2):216-26. doi: 10.1111/imm.12242. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 24467264 Free PMC article.
-
[Selectively activating melanocortin 4 receptor acts against rat sepsis-induced acute liver injury via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Aug;32(8):1055-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27412936 Chinese.
-
Penehyclidine hydrochloride inhibits the release of high-mobility group box 1 in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW264.7 cells and cecal ligation and puncture-induced septic mice.J Surg Res. 2014 Jan;186(1):310-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.08.015. Epub 2013 Sep 8. J Surg Res. 2014. PMID: 24124976
-
Protective Role of Endogenous Kallistatin in Vascular Injury and Senescence by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Dec 2;2018:4138560. doi: 10.1155/2018/4138560. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30622668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Marginal Maternal Zinc Deficiency Produces Liver Damage and Altered Zinc Transporter Expression in Offspring Male Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 May;202(5):2133-2142. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03824-8. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37656390
-
Podocyte-specific soluble epoxide hydrolase deficiency in mice attenuates acute kidney injury.FEBS J. 2017 Jul;284(13):1970-1986. doi: 10.1111/febs.14100. Epub 2017 May 29. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28485854 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing Effects of Oxygen Regulation on Kallistatin Expression: Kallistatin as a Novel Mediator of Oxygen-Induced HIF-1-eNOS-NO Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5262958. doi: 10.1155/2017/5262958. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29387292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variants in SERPINA4 and SERPINA5, but not BCL2 and SIK3 are associated with acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with septic shock.Crit Care. 2017 Mar 8;21(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1631-3. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28270177 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue Kallikrein Exacerbating Sepsis-Induced Endothelial Hyperpermeability is Highly Predictive of Severity and Mortality in Sepsis.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Jul 15;14:3321-3333. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S317874. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34290517 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

