p62/Sequestosome-1, Autophagy-related Gene 8, and Autophagy in Drosophila Are Regulated by Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2 (NRF2), Independent of Transcription Factor TFEB
- PMID: 25931115
- PMCID: PMC4463441
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.656116
p62/Sequestosome-1, Autophagy-related Gene 8, and Autophagy in Drosophila Are Regulated by Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2 (NRF2), Independent of Transcription Factor TFEB
Abstract
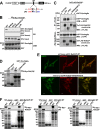
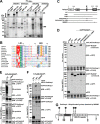
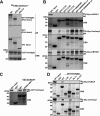
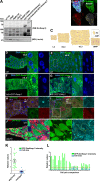
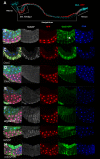
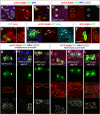
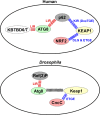
The selective autophagy receptor p62/sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) interacts directly with LC3 and is involved in oxidative stress signaling in two ways in mammals. First, p62 is transcriptionally induced upon oxidative stress by the NF-E2-related factor 2 (NRF2) by direct binding to an antioxidant response element in the p62 promoter. Second, p62 accumulation, occurring when autophagy is impaired, leads to increased p62 binding to the NRF2 inhibitor KEAP1, resulting in reduced proteasomal turnover of NRF2. This gives chronic oxidative stress signaling through a feed forward loop. Here, we show that the Drosophila p62/SQSTM1 orthologue, Ref(2)P, interacts directly with DmAtg8a via an LC3-interacting region motif, supporting a role for Ref(2)P in selective autophagy. The ref(2)P promoter also contains a functional antioxidant response element that is directly bound by the NRF2 orthologue, CncC, which can induce ref(2)P expression along with the oxidative stress-associated gene gstD1. However, distinct from the situation in mammals, Ref(2)P does not interact directly with DmKeap1 via a KEAP1-interacting region motif; nor does ectopically expressed Ref(2)P or autophagy deficiency activate the oxidative stress response. Instead, DmAtg8a interacts directly with DmKeap1, and DmKeap1 is removed upon programmed autophagy in Drosophila gut cells. Strikingly, CncC induced increased Atg8a levels and autophagy independent of TFEB/MitF in fat body and larval gut tissues. Thus, these results extend the intimate relationship between oxidative stress-sensing NRF2/CncC transcription factors and autophagy and suggest that NRF2/CncC may regulate autophagic activity in other organisms too.
Keywords: autophagy; gene transcription; nuclear factor 2 (erythroid-derived 2-like factor) (NFE2L2) (Nrf2); oxidative stress; p62 (sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1)).
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
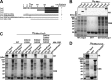

Similar articles
-
p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):22576-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.118976. Epub 2010 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20452972 Free PMC article.
-
P62/SQSTM1 upregulates NQO1 transcription via Nrf2/Keap1a signaling pathway to resist microcystins-induced oxidative stress in freshwater mussel Cristaria plicata.Aquat Toxicol. 2023 Feb;255:106398. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2023.106398. Epub 2023 Jan 14. Aquat Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36669434
-
Loss of ubiquitinated protein autophagy is compensated by persistent cnc/NFE2L2/Nrf2 antioxidant responses.Autophagy. 2022 Oct;18(10):2385-2396. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2037852. Epub 2022 Feb 20. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 35184662 Free PMC article.
-
Novel target for treating Alzheimer's Diseases: Crosstalk between the Nrf2 pathway and autophagy.Ageing Res Rev. 2021 Jan;65:101207. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101207. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Ageing Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33144123 Review.
-
p62 at the interface of autophagy, oxidative stress signaling, and cancer.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Sep 1;17(5):786-93. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4394. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22074114 Review.
Cited by
-
Sqstm1-GFP knock-in mice reveal dynamic actions of Sqstm1 during autophagy and under stress conditions in living cells.J Cell Sci. 2015 Dec 1;128(23):4453-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.180174. Epub 2015 Oct 19. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26483381 Free PMC article.
-
Sequestosome 1/p62: A multitasker in the regulation of malignant tumor aggression (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Oct;59(4):77. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5257. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34414460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of proteostasis by transcription factor NRF2 and impact in neurodegenerative diseases.Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:543-553. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.006. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28104575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nrf1 acts as a highly-conserved determinon for maintaining robust redox homeostasis in the eco-evo-devo process of life histories.Cell Stress. 2025 Jul 7;9:65-142. doi: 10.15698/cst2025.07.306. eCollection 2025. Cell Stress. 2025. PMID: 40703332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of a proteostatic checkpoint in intestinal stem cells contributes to age-related epithelial dysfunction.Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 5;10(1):1050. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08982-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30837466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathers J., Fraser J. A., McMahon M., Saunders R. D., Hayes J. D., McLellan L. I. (2004) Antioxidant and cytoprotective responses to redox stress. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 157–176 - PubMed
-
- Hayes J. D., McMahon M. (2009) NRF2 and KEAP1 mutations: permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 34, 176–188 - PubMed
-
- Taguchi K., Motohashi H., Yamamoto M. (2011) Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in stress response and cancer evolution. Genes Cells 16, 123–140 - PubMed
-
- McMahon M., Itoh K., Yamamoto M., Chanas S. A., Henderson C. J., McLellan L. I., Wolf C. R., Cavin C., Hayes J. D. (2001) The Cap'n'Collar basic leucine zipper transcription factor Nrf2 (NF-E2 p45-related factor 2) controls both constitutive and inducible expression of intestinal detoxification and glutathione biosynthetic enzymes. Cancer Res. 61, 3299–3307 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

