The role of alpha5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in mouse models of chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain
- PMID: 25931144
- PMCID: PMC4600420
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.04.013
The role of alpha5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in mouse models of chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain
Abstract
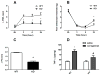
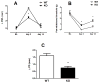
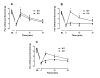
The aim of the present study was to determine the impact of α5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunit deletion in the mouse on the development and intensity of nociceptive behavior in various chronic pain models. The role of α5-containing nAChRs was explored in mouse models of chronic pain, including peripheral neuropathy (chronic constriction nerve injury, CCI), tonic inflammatory pain (the formalin test) and short and long-term inflammatory pain (complete Freund's adjuvant, CFA and carrageenan tests) in α5 knock-out (KO) and wild-type (WT) mice. The results showed that paw-licking time was decreased in the formalin test, and the hyperalgesic and allodynic responses to carrageenan and CFA injections were also reduced. In addition, paw edema in formalin-, carrageenan- or CFA-treated mice were attenuated in α5-KO mice significantly. Furthermore, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) levels of carrageenan-treated paws were lower in α5-KO mice. The antinociceptive effects of nicotine and sazetidine-A but not varenicline were α5-dependent in the formalin test. Both hyperalgesia and allodynia observed in the CCI test were reduced in α5-KO mice. Nicotine reversal of mechanical allodynia in the CCI test was mediated through α5-nAChRs at spinal and peripheral sites. In summary, our results highlight the involvement of the α5 nAChR subunit in the development of hyperalgesia, allodynia and inflammation associated with chronic neuropathic and inflammatory pain models. They also suggest the importance of α5-nAChRs as a target for the treatment of chronic pain.
Keywords: Inflammatory pain; Neuropathic pain; Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; alpha5.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest associated with this study to declare.
Figures
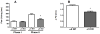
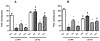
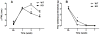

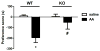
References
-
- Gotti C, Clementi F, Fornari A, Gaimarri A, Guiducci S, Manfredi I, et al. Structural and functional diversity of native brain neuronal nicotinic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;78:703–711. - PubMed
-
- Heinemann S, Boulter J, Deneris E, Conolly J, Duvoisin R, Papke R, et al. The brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family. Prog Brain Res. 1990;86:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Vincler MA, Eisenach JC. Immunocytochemical localization of the alpha3, alpha4, alpha5, alpha7, beta2, beta3 and beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits in the locus coeruleus of the rat. Brain Res. 2003;974:25–36. - PubMed
-
- Genzen JR, Van Cleve W, McGehee DS. Dorsal root ganglion neurons express multiple nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:1773–1782. - PubMed
-
- De Biasi M. Nicotinic receptor mutant mice in the study of autonomic function. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2002;1:331–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

