Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and its distinction from myelodysplastic syndromes
- PMID: 25931582
- PMCID: PMC4624443
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-03-631747
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and its distinction from myelodysplastic syndromes
Abstract
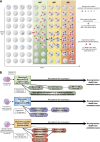
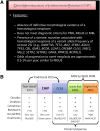
Recent genetic analyses of large populations have revealed that somatic mutations in hematopoietic cells leading to clonal expansion are commonly acquired during human aging. Clonally restricted hematopoiesis is associated with an increased risk of subsequent diagnosis of myeloid or lymphoid neoplasia and increased all-cause mortality. Although myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are defined by cytopenias, dysplastic morphology of blood and marrow cells, and clonal hematopoiesis, most individuals who acquire clonal hematopoiesis during aging will never develop MDS. Therefore, acquisition of somatic mutations that drive clonal expansion in the absence of cytopenias and dysplastic hematopoiesis can be considered clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP), analogous to monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis, which are precursor states for hematologic neoplasms but are usually benign and do not progress. Because mutations are frequently observed in healthy older persons, detection of an MDS-associated somatic mutation in a cytopenic patient without other evidence of MDS may cause diagnostic uncertainty. Here we discuss the nature and prevalence of CHIP, distinction of this state from MDS, and current areas of uncertainty regarding diagnostic criteria for myeloid malignancies.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Clonal hematopoiesis: a "CHIP" off the old block.Blood. 2015 Jul 2;126(1):1-2. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-05-644690. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26138534 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bejar R, Steensma DP. Recent developments in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2014;124(18):2793–2803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

