Abiotic stress induces change in Cinnamoyl CoA Reductase (CCR) protein abundance and lignin deposition in developing seedlings of Leucaena leucocephala
- PMID: 25931776
- PMCID: PMC4411380
- DOI: 10.1007/s12298-015-0289-z
Abiotic stress induces change in Cinnamoyl CoA Reductase (CCR) protein abundance and lignin deposition in developing seedlings of Leucaena leucocephala
Abstract
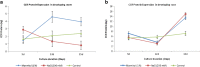
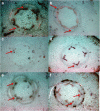
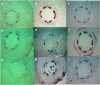
Aboitic stress such as drought and salinity are class of major threats, which plants undergo through their lifetime. Lignin deposition is one of the responses to such abiotic stresses. The gene encoding Cinnamoyl CoA Reductase (CCR) is a key gene for lignin biosynthesis, which has been shown to be over-expressed under stress conditions. In the present study, developing seedlings of Leucaena leucocephala (Vernacular name: Subabul, White popinac) were treated with 1 % mannitol and 200 mM NaCl to mimic drought and salinity stress conditions, respectively. Enzyme linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA) based expression pattern of CCR protein was monitored coupled with Phlorogucinol/HCl activity staining of lignin in transverse sections of developing L. leucocephala seedlings under stress. Our result suggests a differential lignification pattern in developing root and stem under stress conditions. Increase in lignification was observed in mannitol treated stems and corresponding CCR protein accumulation was also higher than control and salt stress treated samples. On the contrary CCR protein was lower in NaCl treated stems and corresponding lignin deposition was also low. Developing root tissue showed a high level of CCR content and lignin deposition than stem samples under all conditions tested. Overall result suggested that lignin accumulation was not affected much in case of developing root however developing stems were significantly affected under drought and salinity stress condition.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; Cinnamoyl CoA reductase; Developing seedlings; Leucaena leucocephala.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression analysis of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR) gene in developing seedlings of Leucaena leucocephala: a pulp yielding tree species.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2011 Feb;49(2):138-45. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21123078
-
Down-regulation of Leucaena leucocephala cinnamoyl CoA reductase (LlCCR) gene induces significant changes in phenotype, soluble phenolic pools and lignin in transgenic tobacco.Plant Cell Rep. 2011 Dec;30(12):2215-31. doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1127-6. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Plant Cell Rep. 2011. PMID: 21847621
-
Comprehensive analysis of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR) gene family in wheat: implications for lignin biosynthesis and stress responses.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 May 1;25(1):567. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06605-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40307683 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in lignin modification: a comprehensive analysis of the effects of genetic manipulations/mutations on lignification and vascular integrity.Phytochemistry. 2002 Oct;61(3):221-94. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(02)00211-x. Phytochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12359514 Review.
-
Lignin biosynthesis and accumulation in response to abiotic stresses in woody plants.For Res (Fayettev). 2022 Jul 12;2:9. doi: 10.48130/FR-2022-0009. eCollection 2022. For Res (Fayettev). 2022. PMID: 39525415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated physiological, metabolomic, and transcriptomic analyses elucidate the regulation mechanisms of lignin synthesis under osmotic stress in alfalfa leaf (Medicago sativa L.).BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 13;25(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10039-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38350871 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of lignin biosynthesis for drought tolerance in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Apr 20;14:1116426. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1116426. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37152118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amino Acid and Carbohydrate Metabolism Are Coordinated to Maintain Energetic Balance during Drought in Sugarcane.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 30;21(23):9124. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239124. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33266228 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and analysis of the transcriptome response to drought in Larix kaempferi using PacBio full-length cDNA sequencing integrated with de novo RNA-seq reads.Planta. 2021 Jan 9;253(2):28. doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03555-3. Planta. 2021. PMID: 33423138
-
Transcriptome characterization of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) seedlings in response to exogenous gibberellin applications.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Jun 20;18(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1336-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 29925317 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
