Continual evolution of type 2 diabetes: an update on pathophysiology and emerging treatment options
- PMID: 25931824
- PMCID: PMC4404882
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S67387
Continual evolution of type 2 diabetes: an update on pathophysiology and emerging treatment options
Abstract
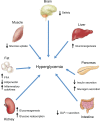
Diabetes is a complex and progressive disease that has a major societal and economic impact. The most common form of diabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), is a multifactorial disease, the pathophysiology of which involves not only the pancreas but also the liver, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, gastrointestinal tract, brain, and kidney. Novel therapies with mechanisms of action that are different from most existing drugs are emerging. One such class consists of compounds that inhibit renal sodium-glucose cotransporter 2, which is responsible for the bulk of glucose reabsorption by the kidneys. This new class of compounds improves glycemic control independently of insulin and promotes weight reduction, providing an additional tool to treat patients with T2DM. This review discusses the underlying pathophysiology of T2DM, clinical guidelines, and available and emerging treatment options, with particular emphasis on sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
Keywords: diabetes; hyperglycemia; oral antidiabetic therapies; pharmacotherapy; sodium-glucose cotransporter 2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of the kidney in hyperglycemia: a new therapeutic target in type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2013 Mar-Apr;28(2):157-65. doi: 10.1097/JCN.0b013e318245633e. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2013. PMID: 22343215
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibition: therapeutic potential for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2013 Jul;29(5):347-56. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2403. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2013. PMID: 23463735 Review.
-
The current role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus management.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 May 25;21(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01512-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35614469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of insulin-dependent and insulin-independent agents for treating patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and potential role for sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors.Postgrad Med. 2013 May;125(3):214-26. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2013.05.2672. Postgrad Med. 2013. PMID: 23748522 Review.
-
Impact of Current and Emerging Glucose-Lowering Drugs on Body Weight in Type 2 Diabetes.Can J Diabetes. 2015 Dec;39 Suppl 5:S148-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.09.090. Can J Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26654858 Review.
Cited by
-
A Synthetic-Biology-Inspired Therapeutic Strategy for Targeting and Treating Hepatogenous Diabetes.Mol Ther. 2017 Feb 1;25(2):443-455. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.008. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28153094 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of Transcriptional Activity of Forkhead Box O1 by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Ameliorates Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetic Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 9;19(11):3539. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113539. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30424007 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic Effect of Tibetan Medicine Tang-Kang-Fu-San in db/db Mice via Activation of PI3K/Akt and AMPK Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Aug 24;8:535. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00535. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28883792 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease: Exploring Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Treatment Strategies.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Dec 11;25(12):436. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2512436. eCollection 2024 Dec. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39742220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving function and potential of pancreatic alpha cells.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Dec;29(6):859-71. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2015.10.002. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26696515 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Atlas. 2013. [Accessed July 10, 2014]. Available from: http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National diabetes statistics report: estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States, 2014. 2014. [Accessed July 16, 2014]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/statsreport14/national-diabetes-report-....
-
- Rowley WR, Bezold C. Creating public awareness: state 2025 diabetes forecasts. Popul Health Manag. 2012;15:194–200. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

