MiR-16 family as potential diagnostic biomarkers for cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 25932099
- PMCID: PMC4402746
MiR-16 family as potential diagnostic biomarkers for cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Cancer is a main public health problem all over the world with its high morbidity and mortality. MicroRNA-16 (miRNA-16, miR-16) family members have been considered as potential biomarkers in cancer diagnosis in several previous studies, but their results were inconsistent.
Objective: The present meta-analysis was conducted to assess the diagnostic efficacy of miR-16 family for cancer systematically.
Methods: Multiple search strategies and random-effects model were used. Pooled sensitivity, specificity and other parameters were calculated. Totally, 1,259 cancer patients and 855 controls from 16 articles were enrolled in this meta-analysis.
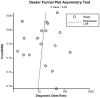
Results: The pooled results for sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratios (PLR), negative likelihood ratios (NLR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and the area under the curve (AUC) were 0.80 (95% CI: 0.73-0.85), 0.77 (95% CI: 0.70-0.84), 3.5 (95% CI: 2.5-5.0), 0.26 (95% CI: 0.19-0.36), 14 (95% CI: 8-25) and 0.86 (95% CI: 0.82-0.88), respectively. Our subgroup analyses indicated miR-16 family assay was more appropriate in Asian populations.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrated that miR-16 family members have a relatively high value as promising biomarkers in diagnosing cancers. Nevertheless, the clinical application of miR-16 family profiling for cancers diagnosis still needs further large-scale studies and additional improvements of substantiation.
Keywords: MicroRNA-16 family; cancer; diagnosis; meta-analysis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-17 family as novel biomarkers for cancer diagnosis: a meta-analysis based on 19 articles.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):6403-11. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4484-x. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26631037
-
MicroRNA panels as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 7;9:915226. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.915226. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36419785 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of microRNA-628 for cancers.J Cancer. 2018 Apr 12;9(9):1623-1634. doi: 10.7150/jca.24193. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29760801 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic values of microRNA-21 in patients with gastric cancer: a meta-analysis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Jan;21(1):120-130. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28121346
-
MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for the Diagnostics of Bladder Cancer: a Meta-Analysis.Clin Lab. 2015;61(8):1101-8. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2015.150204. Clin Lab. 2015. PMID: 26427157 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential of miRNAs in Plasma Extracellular Vesicle for the Stratification of Prostate Cancer in a South African Population.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 4;15(15):3968. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153968. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568783 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased microRNA-181a and -16 expression levels in the labial salivary glands of Sjögren syndrome patients.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jan;15(1):426-432. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5407. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29387196 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on the use of polyaniline and its nanocomposites: a review on recent advances.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Jun 24;186(7):465. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3588-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31236681 Review.
-
MiR-15a/16-1 deficiency induces IL-10-producing CD19+ TIM-1+ cells in tumor microenvironment.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Feb;23(2):1343-1353. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14037. Epub 2018 Nov 23. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30467955 Free PMC article.
-
RGS4 Regulates Proliferation And Apoptosis Of NSCLC Cells Via microRNA-16 And Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Oct 25;12:8701-8714. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S221657. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31695428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levi F, Ferlay J, Galeone C, Lucchini F, Negri E, Boyle P, La Vecchia C. The changing pattern of kidney cancer incidence and mortality in Europe. BJU Int. 2008;101:949–958. - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg B, Cowan NC, Hanbury DC, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, Merseburger AS, Patard JJ, Mulders PF, Sinescu IC. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2010 update. Eur Urol. 2010;58:398–406. - PubMed
-
- Duffy MJ. Role of tumor markers in patients with solid cancers: A critical review. Eur J Intern Med. 2007;18:175–184. - PubMed
-
- Srigley JR, Delahunt B. Uncommon and recently described renal carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 2009;22(Suppl 2):S2–S23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
