Prognostic role of miR-200c in various malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 25932122
- PMCID: PMC4402769
Prognostic role of miR-200c in various malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
MiR-200c expression is dysregulated in various malignancies and may predict the survival of patients with cancer, although the results of different studies conflict. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to resolve this discrepancy. We queried the PubMed and Embase using multiple search strategies. Data were extracted from studies comparing overall survival and progression-free survival in patients with cancer with high and low levels of miR-200c expression. Fixed and random models were used where appropriate. A combined hazards ratio (HR) was calculated to estimate the association of high levels of miR-200c with survival. We selected 16 studies of 1485 participants for our final meta-analysis. Upregulated expression of miR-200c predicted significantly worse overall survival in patients with cancer (HR 1.51; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.06-2.16, P = 0.023). Subgroup analysis indicated that high levels of miR-200c was associated with decreased survival of Caucasians and patients with gynecological tumors with pooled HR values of 1.82 (95% CI 1.27-2.26, P = 0.01) and 3.23 (95% CI 1.11-9.38, P = 0.032), respectively. Because of the absence of apparent heterogeneity, the combined HRs were 1.69 (95% CI 1.24-2.30, P = 0.001) for squamous cell carcinoma and 1.91 (95% CI 1.40-2.59, P < 0.001) for samples from peripheral blood. Increased expression of miR-200c significantly associated with shorter progression-free survival of patients with cancer (HR 2.37; 95% CI 1.47-3.81, P < 0.001). Our meta-analysis indicates that the level of miR-200c expression predicted survival of patients with cancer, particularly for Caucasians and patients with gynecological cancer. Increased expression of miR-200c predicted shorter survival of patients with squamous cell carcinomas. Our findings indicate that monitoring the levels of miR-200c in blood may be useful for following tumor progression as well as patients' prognosis.
Keywords: Prognosis; cancers; meta-analysis; miR-200c; survival.
Figures
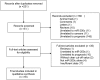
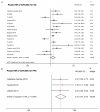


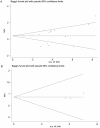
Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of microRNA-200c in various types of cancer: An updated meta-analysis of 34 studies.Mol Clin Oncol. 2016 Jun;4(6):933-941. doi: 10.3892/mco.2016.842. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27284426 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-200 families and prognostic value in various carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Aging Med (Milton). 2018 Feb 7;1(1):39-45. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12005. eCollection 2018 Jun. Aging Med (Milton). 2018. PMID: 31942478 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance Role of microRNA-200c as a Prognostic Factor in Various Human Solid Malignant Neoplasms: A Meta-Analysis.J Cancer. 2019 Jan 1;10(1):277-286. doi: 10.7150/jca.27536. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30662548 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative data mining and meta-analysis to investigate the prognostic role of microRNA-200 family in various human malignant neoplasms: A consideration on heterogeneity.Gene. 2019 Oct 20;716:144025. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144025. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31394177 Review.
-
Prognostic Value and Clinicopathology Significance of MicroRNA-200c Expression in Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 2;10(6):e0128642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128642. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26035744 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the miRNA expression profiles in fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tonsillar tumors.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 23;12(6):e0179645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179645. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28644855 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated expression of miR-421 is associated with poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Aug 13;10:2627-2633. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S167432. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30147363 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
