Association between RAD51 polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility: a meta analysis
- PMID: 25932169
- PMCID: PMC4402816
Association between RAD51 polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility: a meta analysis
Abstract
Background: RAD51 interacting with BRCA1 and BRCA2 could modulate the penetrance of BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations, which may increase susceptibility for breast cancer by inhibiting DNA repair and genome stability. The purpose of this study was to provide refined statistical evidence for the association between RAD51 polymorphism and breast cancer risk.
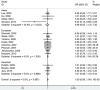
Design and results: We conducted a meta-analysis of 15 publications with a total of 11,766 cancer cases and 11,227 controls. We summarized the data on the association of RAD51 polymorphism with breast cancer risk and performed subgroup analyses by ethnicity and control source. The pooled ORs based on fixed-effects model did not indicate a modified risk of breast cancer associated with RAD51 polymorphism in the overall population. Nor did we find a significant association in any stratified analysis.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis suggested that RAD51 polymorphism did not appear to represent a significant risk factor for breast cancer.
Keywords: RAD51; breast cancer; polymorphism; susceptibility.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association between the RAD51 135 G>C polymorphism and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis of 19,068 cases and 22,630 controls.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 9;8(9):e75153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075153. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040396 Free PMC article.
-
A single nucleotide polymorphism in the 5' untranslated region of RAD51 and risk of cancer among BRCA1/2 mutation carriers.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001 Sep;10(9):955-60. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001. PMID: 11535547
-
RAD51 135G>C polymorphism and risk of familial breast cancer in a South American population.Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007 Oct 1;178(1):65-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2007.05.024. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007. PMID: 17889711
-
Association between the BRCA2 rs144848 polymorphism and cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 13;8(24):39818-39832. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16242. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28418854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between BRCA1 rs799917 polymorphism and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis of 19,878 subjects.Biomed Pharmacother. 2014 Sep;68(7):905-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 25194442 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and genetic characterization of hereditary breast cancer in a Chinese population.Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2017 Oct 30;15:19. doi: 10.1186/s13053-017-0079-4. eCollection 2017. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 29093764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pedraza AM, Pollan M, Pastor-Barriuso R, Cabanes A. Disparities in breast cancer mortality trends in a middle income country. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;134:1199–1207. - PubMed
-
- Hortobagyi GN, de la Garza Salazar J, Pritchard K, Amadori D, Haidinger R, Hudis CA, Khaled H, Liu MC, Martin M, Namer M, O’Shaughnessy JA, Shen ZZ, Albain KS. The global breast cancer burden: variations in epidemiology and survival. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005;6:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman DA, Lonstein JE, Morin MM, Visscher W, Harris BS 3rd, Boice JD Jr. Breast cancer in women with scoliosis exposed to multiple diagnostic x rays. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989;81:1307–1312. - PubMed
-
- Gietko M. [Hiatal hernia in children with diseases and injuries of the central nervous system] . Pediatr Pol. 1977;52:177–181. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
