Lentivirus-mediated TPD52L2 depletion inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells in vitro
- PMID: 25932170
- PMCID: PMC4402817
Lentivirus-mediated TPD52L2 depletion inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells in vitro
Retraction in
- Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016; 9(6): 12416
-
Lentivirus-mediated TPD52L2 depletion inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells in vitro [Retraction].Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016 Jun 15;9(6):12416. eCollection 2016. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 29874322 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Tumor protein D52-like 2, known as hD54 in previous studies (TPD52L2), is a member of TPD52 family which has been implicated in multiple human cancers. In recent reports, TPD52 proteins were indicated to be associated with several malignancies, but very little is known about the function of TPD52L2 in liver cancers. In our present study, in order to explore the role of TPD52L2 in liver cancer, TPD52L2 was knocked down in SMMC-7721 liver cancer cell line by lentivirus mediated RNA interference. The results demonstrated that depletion of TPD52L2 could remarkably inhibit proliferation and colony forming ability of cancer cell SMMC-7721. Furthermore, cell cycle in TPD52L2 depleted cells was verified to be arrested in G0/G1 phase as determined by FACS assay, in consistence with the observation of cell proliferation inhibition. These results unraveled that TPD52L2 played an important role in tumorigenesis pathways of liver cancer and might serve as a promising target in human liver cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Keywords: RNA interference; TPD52L2; lentivirus; liver cancer; proliferation.
Figures
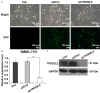


Similar articles
-
Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of tumor protein D52-like 2 inhibits glioma cell proliferation.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2014 May 11;60(1):39-44. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2014. PMID: 24842331
-
Tumor protein D52-like 2 contributes to proliferation of breast cancer cells.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2015 Feb;30(1):1-7. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2014.1723. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2015. Retraction in: Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017 Dec;32(10):387. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2014.1723.retract. PMID: 25629696 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Tumor protein D52-like 2 accelerates gastric cancer cell proliferation in vitro.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2015 Apr;30(3):111-6. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2014.1766. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2015. Retraction in: Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017 Dec;32(10):388. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2014.1766.retract. PMID: 25746840 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Knockdown of tumor protein D52-like 2 induces cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Biol Int. 2015 Mar;39(3):264-71. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10388. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Cell Biol Int. 2015. Retraction in: Cell Biol Int. 2016 Mar;40(3):361. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10593. PMID: 25262828 Retracted.
-
MicroRNA-217 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting Tpd52l2 in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2017 Dec;38(6):3567-3573. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.6036. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29039566
Cited by
-
Increased expression of tumor protein D54 is associated with clinical progression and poor prognosis in patients with prostate cancer.Oncol Lett. 2017 Dec;14(6):7739-7744. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7214. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29250174 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of TPD52L2 in HNSCC: prognostic significance and correlation with immune infiltrates.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 7;24(1):1191. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04977-1. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39375696 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-503 suppresses the migration, proliferation and colony formation of prostate cancer cells by targeting tumor protein D52 like 2.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jan;15(1):473-478. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5401. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29375699 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Vector-Based Melanoma Gene Therapy.Biomedicines. 2020 Mar 16;8(3):60. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8030060. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32187995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive study based on exosome-related immunosuppression genes and tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Dec 22;22(1):1344. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10463-0. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36550445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Barker-Collo S, Bartels DH, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bhalla K, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Boufous S, Bucello C, Burch M, Burney P, Carapetis J, Chen H, Chou D, Chugh SS, Coffeng LE, Colan SD, Colquhoun S, Colson KE, Condon J, Connor MD, Cooper LT, Corriere M, Cortinovis M, de Vaccaro KC, Couser W, Cowie BC, Criqui MH, Cross M, Dabhadkar KC, Dahodwala N, De Leo D, Degenhardt L, Delossantos A, Denenberg J, Des Jarlais DC, Dharmaratne SD, Dorsey ER, Driscoll T, Duber H, Ebel B, Erwin PJ, Espindola P, Ezzati M, Feigin V, Flaxman AD, Forouzanfar MH, Fowkes FG, Franklin R, Fransen M, Freeman MK, Gabriel SE, Gakidou E, Gaspari F, Gillum RF, Gonzalez-Medina D, Halasa YA, Haring D, Harrison JE, Havmoeller R, Hay RJ, Hoen B, Hotez PJ, Hoy D, Jacobsen KH, James SL, Jasrasaria R, Jayaraman S, Johns N, Karthikeyan G, Kassebaum N, Keren A, Khoo JP, Knowlton LM, Kobusingye O, Koranteng A, Krishnamurthi R, Lipnick M, Lipshultz SE, Ohno SL, Mabweijano J, MacIntyre MF, Mallinger L, March L, Marks GB, Marks R, Matsumori A, Matzopoulos R, Mayosi BM, McAnulty JH, McDermott MM, McGrath J, Mensah GA, Merriman TR, Michaud C, Miller M, Miller TR, Mock C, Mocumbi AO, Mokdad AA, Moran A, Mulholland K, Nair MN, Naldi L, Narayan KM, Nasseri K, Norman P, O’Donnell M, Omer SB, Ortblad K, Osborne R, Ozgediz D, Pahari B, Pandian JD, Rivero AP, Padilla RP, Perez-Ruiz F, Perico N, Phillips D, Pierce K, Pope CA 3rd, Porrini E, Pourmalek F, Raju M, Ranganathan D, Rehm JT, Rein DB, Remuzzi G, Rivara FP, Roberts T, De Leon FR, Rosenfeld LC, Rushton L, Sacco RL, Salomon JA, Sampson U, Sanman E, Schwebel DC, Segui-Gomez M, Shepard DS, Singh D, Singleton J, Sliwa K, Smith E, Steer A, Taylor JA, Thomas B, Tleyjeh IM, Towbin JA, Truelsen T, Undurraga EA, Venketasubramanian N, Vijayakumar L, Vos T, Wagner GR, Wang M, Wang W, Watt K, Weinstock MA, Weintraub R, Wilkinson JD, Woolf AD, Wulf S, Yeh PH, Yip P, Zabetian A, Zheng ZJ, Lopez AD, Murray CJ, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2095–2128. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Luke C, Price T, Roder D. Epidemiology of cancer of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts in an Australian population. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2010;11:1479–1485. - PubMed
-
- Katanoda K, Matsuda T. Five-year relative survival rate of liver cancer in the USA, Europe and Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014;44:302–303. - PubMed
-
- Li G, Xiao Z, Liu J, Li C, Li F, Chen Z. Cancer: a proteomic disease. Sci China Life Sci. 2011;54:403–408. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
