Systemic side effects of locally used oxymetazoline
- PMID: 25932218
- PMCID: PMC4402865
Systemic side effects of locally used oxymetazoline
Abstract
Objectives: The object of the study is to experimentally investigate the possible systemic side effects of Oxymetazoline including its nasal spray which has been in use for a long time both by the physicians and patients. There is no study in the literature to address the damages of oxymetazoline on the end organ.
Materials and methods: The study conducted on 2 groups of rat. Group 1 (n = 8): Control; and Group 2 (n = 8): Oxymetazoline. During 4 week, the control group was applied with 2 drops of saline water on each nasal cavity 3 times a day and the other group was applied with 2 drops of oxymetazoline HCl 3 times a day. At the end of experiment, samples from mandible, parotid and tails of the rats were taken in 10% formalin for histopathological investigations.
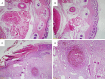
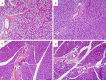
Results: In histopathological experiments, when compared with the control group, the oxymetazoline group showed significant increase in many of the histopathological parameters (ischemic changes: P = 0.0001; congestion: P = 0.0006; arterial thrombosis: P = Ns; PNL accumulations: P = 0.001; necrosis: P = 0.0001; and ulceration: P = 0.014). The results of histopathologic tests on the samples taken from mandible and parotid gland, in comparison with the control group, showed no significant increase (focal inflammation: P = Ns; and lymphocyte aggregation: P = Ns).
Conclusion: Due to the damage that the long-term use of nasal spray including oxymetazoline, it may cause injury on the end organ, which we revealed in our histopathological experiments. We believe that it's essential for the physicians to provide information on the side effects of the medicine to their patients who use for a long term.
Keywords: Nasal spray; end-organ injury; oxymetazoline; systemic side effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of oxymetazoline nasal spray on intraocular pressure and retrobulbar hemodynamics.J Otolaryngol. 2006 Feb;35(1):30-5. doi: 10.2310/7070.2005.4102. J Otolaryngol. 2006. PMID: 16527014 Clinical Trial.
-
Four-week use of oxymetazoline nasal spray (Nezeril) once daily at night induces rebound swelling and nasal hyperreactivity.Acta Otolaryngol. 1995 Jan;115(1):71-5. doi: 10.3109/00016489509133350. Acta Otolaryngol. 1995. PMID: 7762389 Clinical Trial.
-
Premedication Methods in Nasal Endoscopy: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind Study.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Jun;10(2):158-163. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2016.00563. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27459198 Free PMC article.
-
Anesthetic Efficacy of Intranasal 3% Tetracaine plus 0.05% Oxymetazoline (Kovanaze) in Maxillary Teeth.J Endod. 2019 Mar;45(3):257-262. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2018.12.003. J Endod. 2019. PMID: 30803532 Clinical Trial.
-
Benzalkonium chloride in nasal decongestive sprays has a long-lasting adverse effect on the nasal mucosa of healthy volunteers.Clin Exp Allergy. 1995 May;25(5):401-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1995.tb01070.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 1995. PMID: 7553242 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Half Percent Oxymetazoline Nasal Drops on Post-Tonsillectomy Cough, Sore Throat and Bleeding in Children; A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial.Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Jul 27;12:193. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_247_22. eCollection 2023. Adv Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 37694249 Free PMC article.
-
Nasoseptal Perforation: from Etiology to Treatment.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018 Feb 5;18(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s11882-018-0754-1. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018. PMID: 29404797 Review.
-
Ischemic Stroke Associated with Chronic Xylometazoline Nasal Spray Misuse: A Rare Avoidable Adverse Event.Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2021 Mar-Apr;24(2):304-307. doi: 10.4103/aian.AIAN_291_20. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34220102 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Conceptual Model for Using Imidazoline Derivative Solutions in Pulpal Management.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 15;10(6):1212. doi: 10.3390/jcm10061212. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33803990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal drug delivery: opportunities and toxicologic challenges during drug development.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Apr;12(4):735-757. doi: 10.1007/s13346-020-00891-5. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 33491126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doshi J. Rhinitis medicamentosa: what an otolaryngologist needs to know. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266:623–625. - PubMed
-
- Ramey JT, Bailen E, Lockey RF. Rhinitis medicamentosa. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2006;16:148–155. - PubMed
-
- Abruzzo T, Patino M, Leach J, Rahme R, Geller J. Cerebral vasoconstriction triggered by sympathomimetic drugs during intra-atrerial chemotherapy. Pediatr Neurol. 2013;48:139–142. - PubMed
-
- Alpay A, Ermis B, Ugurbas SC, Battal F, Sagdik HM. The local vasoconstriction of infant’s skin following instillation of mydriatic eye drops. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;66:1161–1164. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
