Comparable outcomes for β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations and carbapenems in definitive treatment of bloodstream infections caused by cefotaxime-resistant Escherichia coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 25932324
- PMCID: PMC4414382
- DOI: 10.1186/s13756-015-0055-6
Comparable outcomes for β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations and carbapenems in definitive treatment of bloodstream infections caused by cefotaxime-resistant Escherichia coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
Background: Extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing Enterobacteriaceae are often susceptible in vitro to β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor (BLBLI) combination antibiotics, but their use has been limited by concerns of clinical inefficacy. We aimed to compare outcomes between patients treated with BLBLIs and carbapenems for bloodstream infection (BSI) caused by cefotaxime non-susceptible (likely ESBL- or AmpC β-lactamase-producing) Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
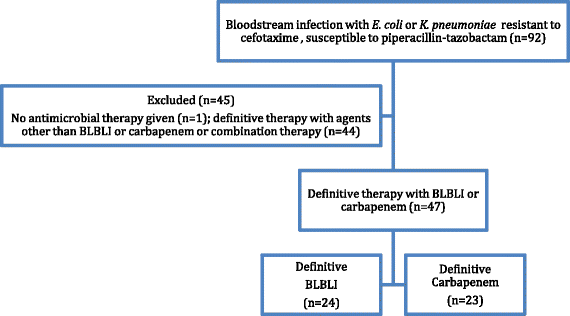
Methods: All adult patients with a BSI caused by cefotaxime non-susceptible E. coli or K. pneumoniae were included from May 2012-May 2013. We compared outcomes between patients who had definitive monotherapy with a carbapenem to those who had definitive monotherapy with a BLBLI.
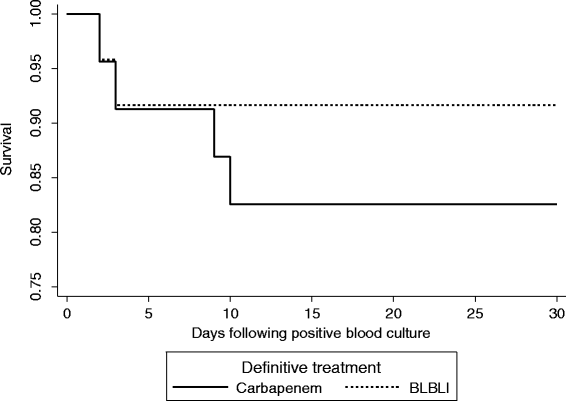
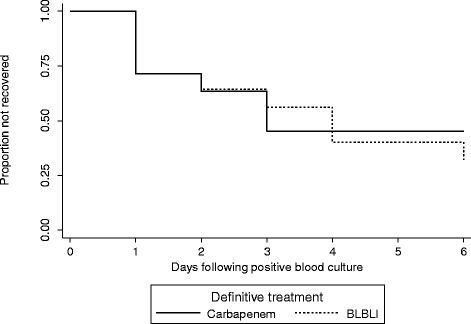
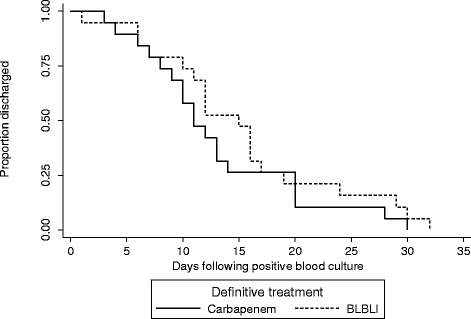
Results: There were 92 BSIs that fulfilled the microbiological inclusion criteria. 79 (85.9%) were caused by E. coli and 13 (14.1%) by K. pneumoniae. Four out of 23 (17.4%) patients treated with carbapenem monotherapy and 2 out of 24 (8.3%) patients treated with BLBLI monotherapy died (adjusted HR for survival 0.91, 95% CI 0.13 to 6.28; p = 0.92). The time to resolution of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria did not vary between the treatment groups (adjusted HR 0.91, 95% CI 0.32 to 2.59; p = 0.97). The length of hospital admission post-positive blood culture was slightly longer in patients treated with BLBLIs (median duration 15 vs. 11 days), although this was not significant (adjusted HR 0.62; 95% CI 0.27 to 1.42; p = 0.26). There were no significant differences in subsequent isolation of carbapenem resistant organisms (4.3% vs. 4.2%, p = 1.0), C. difficile infection (13.0% vs. 8.3%, p = 0.67) or relapsed BSI (0% vs. 2%, p = 0.23).
Conclusions: BLBLIs appear to have a similar efficacy to carbapenems in the treatment of cefotaxime-resistant E. coli and K. pneumoniae bloodstream infections. Directed therapy with a BLBLI, when susceptibility is proven, may represent an appropriate carbapenem-sparing option.
Keywords: Carbapenem; Enterobacteriaceae; Extended-spectrum β-lactamase; Piperacillin-tazobactam.
Figures
Similar articles
-
β-Lactam/β-lactam inhibitor combinations for the treatment of bacteremia due to extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli: a post hoc analysis of prospective cohorts.Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Jan 15;54(2):167-74. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir790. Epub 2011 Nov 4. Clin Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22057701
-
Risk factors and outcomes in non-transplant patients with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli bacteremia: a retrospective study from 2013 to 2016.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2019 Aug 27;8:144. doi: 10.1186/s13756-019-0599-y. eCollection 2019. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2019. PMID: 31467670 Free PMC article.
-
[Empirical therapy of bloodstream infections caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jul 12;96(26):2076-80. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.26.008. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27468620 Chinese.
-
β-lactam and β-lactamase inhibitor combinations in the treatment of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae: time for a reappraisal in the era of few antibiotic options?Lancet Infect Dis. 2015 Apr;15(4):475-85. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70950-8. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25716293 Review.
-
Carbapenem-sparing beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitors versus carbapenems for bloodstream infections caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2023 Mar;128:194-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.01.001. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Int J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36621752
Cited by
-
Empiric Therapy With Carbapenem-Sparing Regimens for Bloodstream Infections due to Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae: Results From the INCREMENT Cohort.Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Oct 30;65(10):1615-1623. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix606. Clin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29020250 Free PMC article.
-
Carbapenem-Sparing Strategies for ESBL Producers: When and How.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Feb 5;9(2):61. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9020061. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32033322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms in Gram-Negative Bacteria.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Nov 3;12(11):1590. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12111590. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piperacillin-tazobactam as alternative to carbapenems for ICU patients.Ann Intensive Care. 2017 Nov 10;7(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0334-x. Ann Intensive Care. 2017. PMID: 29127502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates in the Management of Cephalosporin-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2016 Dec;18(12):39. doi: 10.1007/s11908-016-0552-7. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2016. PMID: 27743202 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

