Breast 3 T-MR imaging: indication for stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy
- PMID: 25932356
- PMCID: PMC4409605
- DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-481
Breast 3 T-MR imaging: indication for stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to assess indications for stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVAB) evaluated by breast 3 T-magnetic resonance (3 T-MR) imaging in patients showing suspicious microcalcifications on mammography and negative ultrasound (US) findings.
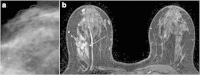
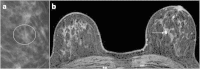
Methods and materials: Fifty-five patients with 55 breast lesions showing suspicious microcalcifications on mammography and negative US findings underwent preoperative 3 T-MR examination including dynamic MR imaging. All patients underwent SVAB within 1 month of MR imaging. The pathological diagnosis of each breast lesion was made by examining tissues obtained by SVAB or radical/partial mastectomy. 3 T-MR imaging findings were evaluated by using the American College of Radiology Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System Atlas (BI-RADS-MRI) and then were correlated with the histopathological findings. When BI-RADS 4 and 5 MR imaging lesions were assumed to be malignant, the usefulness of 3 T-MR imaging was evaluated for diagnosis of impalpable breast lesions by SVAB among lesions with microcalcification detected by mammography and negative US findings.
Results: There were 21 malignant lesions, including 5 invasive ductal carcinomas, 16 lesions of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy of 3 T-MR imaging for deciding the indications for SVAB was 90.5%, 97.1%, 95.0%, 94.3%, and 94.5%, respectively. The one-false negative case was a DCIS with small enhancing lesions (0.5 mm). The one false-positive case was ductal adenoma with a linear ductal pattern of enhancement.
Conclusions: 3 T-MR imaging may be useful for deciding the indications for SVAB in patients who have breast lesions with microcalcification that are impalpable and are detected by mammography and negative US findings. However, our findings should be considered preliminary and further prospective investigation is required.
Keywords: 3 T-MR imaging; Breast cancer; Mammography; Microcalcifications; Stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging in screening detected microcalcification lesions of the breast: is there any value?Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007 Jul;103(3):269-81. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9373-y. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007. PMID: 17063274
-
Evaluation of the stereotactic 8G vacuum-assisted breast biopsy in the histologic evaluation of suspicious mammography findings (BI-RADS IV).Invest Radiol. 2005 Jul;40(7):465-71. doi: 10.1097/01.rli.0000167711.78180.a9. Invest Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15973139
-
Contrast-enhanced MR imaging in patients with BI-RADS 3-5 microcalcifications.Radiol Med. 2007 Mar;112(2):272-86. doi: 10.1007/s11547-007-0141-9. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Radiol Med. 2007. PMID: 17361370 English, Italian.
-
Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB).Ann Oncol. 2004 Mar;15(3):450-4. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdh088. Ann Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14998847 Review.
-
Stereotactic 14 gauge core-biopsy of the breast: results from 101 patients.Aust N Z J Surg. 1996 Sep;66(9):585-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1996.tb00824.x. Aust N Z J Surg. 1996. PMID: 8859155 Review.
Cited by
-
US and MRI in the evaluation of mammographic BI-RADS 4 and 5 microcalcifications.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018 Jul;24(4):187-194. doi: 10.5152/dir.2018.17414. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30091708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American College of Radiology . Illustrated Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 4. American College of Radiology: Reston; 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

