Diagnostic value of plain abdominal radiography in stroke patients with bowel dysfunction
- PMID: 25932421
- PMCID: PMC4414971
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2015.39.2.243
Diagnostic value of plain abdominal radiography in stroke patients with bowel dysfunction
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic value of plain abdominal radiography in stroke patients with bowel dysfunction.
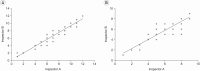
Methods: A total of 59 stroke patients were recruited and assigned into constipation or non-constipation group. Patients were interviewed to obtain clinical information, constipation score, and Bristol stool form scale. The total and segmental colon transit time (CTT) was measured using radio-opaque markers (Kolomark). The degree of stool retention was evaluated by plain abdominal radiography and scored by two different methods (Starreveld score and Leech score). The relationship between the clinical aspects, CTT, and stool retention score using plain abdominal radiography was determined.
Results: Average constipation score was 4.59±2.16. Average Bristol stool form scale was 3.86±1.13. The total and segmental CTTs showed significant differences between the constipation and non-constipation groups. There was statistically significant (p<0.05) correlation between the total CTT and constipation score or between Starreveld score and Leech score. Each segmental CTT showed significant correlation (p<0.05) between segmental stool retention scores.
Conclusion: The stool retention score showed significant correlation with constipation score as well as total and segmental CTT. Thus, plain abdominal radiography is a simple and convenient method for the evaluation of bowel dysfunction in stroke patients.
Keywords: Abdominal radiography; Colon transit time; Constipation; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Plain abdominal radiograph as an evaluation method of bowel dysfunction in patients with spinal cord injury.Ann Rehabil Med. 2013 Aug;37(4):547-55. doi: 10.5535/arm.2013.37.4.547. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013. PMID: 24020036 Free PMC article.
-
Bowel dysfunction and colon transit time in brain-injured patients.Ann Rehabil Med. 2012 Jun;36(3):371-8. doi: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.371. Epub 2012 Jun 30. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012. PMID: 22837973 Free PMC article.
-
Defaecation disorders in children, colonic transit time versus the Barr-score.Eur J Pediatr. 1995 Apr;154(4):277-84. doi: 10.1007/BF01957362. Eur J Pediatr. 1995. PMID: 7607277
-
Faecal retention: a common cause in functional bowel disorders, appendicitis and haemorrhoids--with medical and surgical therapy.Dan Med J. 2015 Mar;62(3):B5031. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25748875
-
Simple diagnostic approach to childhood fecal retention using the Leech score and Bristol stool form scale in medical practice.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Feb;25(2):334-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06015.x. Epub 2009 Oct 9. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 19817956
Cited by
-
Visceral Mobilization and Functional Constipation in Stroke Survivors: A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind, Clinical Trial.Cureus. 2020 May 11;12(5):e8058. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8058. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32537276 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Related Factors of Hypokalemia in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Nov 30;17:5697-5705. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S492025. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39635664 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of constipation in stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun;96(25):e7225. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007225. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28640117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scivoletto G, Fuoco U, Badiali D, Braccl F, Lucente LD, Patrelli A, et al. Gastrointestinal dysfunction following stroke. J Neurol Sci. 1997;150:S151.
-
- Robain G, Chennevelle JM, Petit F, Piera JB. Incidence of constipation after recent vascular hemiplegia: a prospective cohort of 152 patients. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2002;158(5 Pt 1):589–592. - PubMed
-
- Harari D, Norton C, Lockwood L, Swift C. Treatment of constipation and fecal incontinence in stroke patients: randomized controlled trial. Stroke. 2004;35:2549–2555. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf W, Park F, Lof J, Quigley EM. An examination of the reliability of reported stool frequency in the diagnosis of idiopathic constipation. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:26–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

