Prohibitin Is Involved in Patients with IgG4 Related Disease
- PMID: 25932630
- PMCID: PMC4416882
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125331
Prohibitin Is Involved in Patients with IgG4 Related Disease
Abstract
Objective: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a chronic systemic disease involved in many organs and tissues. As only limited autoantigens have been found since the beginning of this century, the aim of this study was to reveal new candidate autoantigens of IgG4-RD.
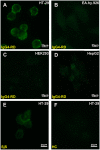
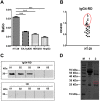
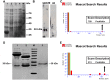
Methods: Multiple cell lines including HT-29, EA.hy926, HEK 293 and HepG2 were used to test the binding ability of circulating autoantibodies from IgG4-RD sera. The amino-acid sequence was then analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight tandem (MALDI-TOF/TOF) mass spectrometry. After the cloning and expression of recombinant putative autoantigen in a bacterial expression system, the corresponding immuno assay was set up and utilized to observe the prevalence of serum autoantibodies in a large set of confirmed clinical samples.
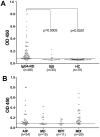
Results: One positive autoantigen was identified as prohibitin. ELISA analysis showed that a majority of patients with IgG4-RD have antibodies against prohibitin. Anti-prohibitin antibodies were present in the sera of patients with definite autoimmune pancreatitis (25/34; 73.5%), Mikulicz's disease (8/15; 53.3%), retroperitoneal fibrosis (6/11; 54.5%), other probable IgG4-RD (26/29; 89.7%) and Sjögren's syndrome (4/30; 13.3%) but not in apparently healthy donors (1/70; 1.4%).
Conclusions: An association between prohibitin and patients with some IgG4-RD was observed, although the results were quite heterogeneous among different individuals within autoimmune pancreatitis, Mikulicz's disease and retroperitoneal fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Deshpande V, Chicano S, Finkelberg D, Selig MK, Mino-Kenudson M, Brugge WR, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis: a systemic immune complex mediated disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30: 1537–1545. - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi K, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Tabata I, Fujita N. Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis with cholangitis: a variant of primary sclerosing cholangitis extensively involving pancreas. Hum Pathol. 1991;22: 387–395. - PubMed
-
- Masaki Y, Kurose N, Umehara H. IgG4-related disease: a novel lymphoproliferative disorder discovered and established in Japan in the 21st century. J Clin Exp Hematopathol. 2011;51: 13–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

