Effects of cordycepin on the microglia-overactivation-induced impairments of growth and development of hippocampal cultured neurons
- PMID: 25932642
- PMCID: PMC4416906
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125902
Effects of cordycepin on the microglia-overactivation-induced impairments of growth and development of hippocampal cultured neurons
Abstract
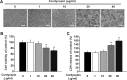
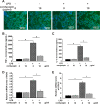
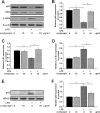
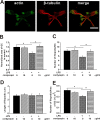
Microglial cells are normally activated in response to brain injury or immunological stimuli to protect central nervous system (CNS). However, over-activation of microglia conversely amplifies the inflammatory effects and mediates cellular degeneration, leading to the death of neurons. Recently, cordycepin, an active component found in Cordyceps militarisa known as a rare Chinese caterpillar fungus, has been reported as an effective drug for treating inflammatory diseases and cancer via unclear mechanisms. In this study, we attempted to identify the anti-inflammatory role of cordycepin and its protective effects on the impairments of neural growth and development induced by microglial over-activation. The results indicate that cordycepin could attenuate the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced microglial activation, evidenced by the dramatically reduced release of TNF-α and IL-1β, as well as the down-regulation of mRNA levels of iNOS and COX-2 after cordycepin treatment. Besides, cordycepin reversed the LPS-induced activation of NF-κB pathway, resulting in anti-inflammatory effects. Furthermore, by employing the conditioned medium (CM), we found cordycepin was able to recover the impairments of neural growth and development in the primary hippocampal neurons cultured in LPS-CM, including cell viability, growth cone extension, neurite sprouting and outgrowth as well as spinogenesis. This study expands our knowledge of the anti-inflammatory function of cordycepin and paves the way for the biomedical applications of cordycepin in the therapies of neural injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tanshinone IIA Rescued the Impairments of Primary Hippocampal Neurons Induced by BV2 Microglial Over-Activation.Neurochem Res. 2015 Jul;40(7):1497-508. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1624-z. Epub 2015 May 27. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 26012368
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin via suppression of inflammatory mediators in BV2 microglial cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Dec;10(12):1580-6. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.09.011. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20937401
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-κB signaling pathways.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Oct 16;8:1941-53. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S71957. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25342887 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of cordycepin emphasizing its potential against neuroinflammation: An update.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 5;908:174364. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174364. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34297967 Review.
-
The Role of Autophagy in Anti-Cancer and Health Promoting Effects of Cordycepin.Molecules. 2021 Aug 16;26(16):4954. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164954. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unique Bioactives from Zombie Fungus (Cordyceps) as Promising Multitargeted Neuroprotective Agents.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 27;16(1):102. doi: 10.3390/nu16010102. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38201932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mushroom-derived bioactive components with definite structures in alleviating the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 21;15:1373660. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1373660. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38835656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A formulation of combined Poria cocos and Cordyceps militaris rice ameliorates depressive-like effects by downregulating p38 MAPK signaling pathways.J Tradit Complement Med. 2024 May 16;15(4):414-422. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.05.002. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Tradit Complement Med. 2024. PMID: 40677543 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of cordycepin inhibit glutamate-induced apoptosis in hippocampal neurons.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024 Feb;29(1):10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cstres.2024.01.001. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2024. PMID: 38219840 Free PMC article.
-
Cordycepin protects against β-amyloid and ibotenic acid-induced hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neuronal hyperactivity.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019 Nov;23(6):483-491. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.6.483. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31680770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gai G-z, Jin S-j, Wang B, Li Y, Li C. The efficacy of Cordyceps militaris capsules in treatment of chronic bronchitis in comparison with Jinshuibao capsules. Chinese new drugs journal. 2004;13:169–70.
-
- Deitch AD, Sawicki SG. Effects of cordycepin on microtubules of cultured mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979;118(1):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Yun YH, Lee SJ, Lee CK, Kim KJ. Anti-diabetic effects of CCCA, CMKSS, and cordycepin from Cordyceps militaris and the immune responses in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Natural Product Sciences. 2003;9(4):291–8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

