Gene-wise association of variants in four lysosomal storage disorder genes in neuropathologically confirmed Lewy body disease
- PMID: 25933391
- PMCID: PMC4416714
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125204
Gene-wise association of variants in four lysosomal storage disorder genes in neuropathologically confirmed Lewy body disease
Abstract
Objective: Variants in GBA are associated with Lewy Body (LB) pathology. We investigated whether variants in other lysosomal storage disorder (LSD) genes also contribute to disease pathogenesis.
Methods: We performed a genetic analysis of four LSD genes including GBA, HEXA, SMPD1, and MCOLN1 in 231 brain autopsies. Brain autopsies included neuropathologically defined LBD without Alzheimer Disease (AD) changes (n = 59), AD without significant LB pathology (n = 71), Alzheimer disease and lewy body variant (ADLBV) (n = 68), and control brains without LB or AD neuropathology (n = 33). Sequencing of HEXA, SMPD1, MCOLN1 and GBA followed by 'gene wise' genetic association analysis was performed. To determine the functional effect, a biochemical analysis of GBA in a subset of brains was also performed. GCase activity was measured in a subset of brain samples (n = 64) that included LBD brains, with or without GBA mutations, and control brains. A lipidomic analysis was also performed in brain autopsies (n = 67) which included LBD (n = 34), ADLBV (n = 3), AD (n = 4), PD (n = 9) and control brains (n = 17), comparing GBA mutation carriers to non-carriers.
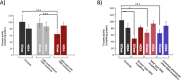
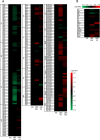
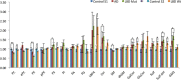
Results: In a 'gene-wise' analysis, variants in GBA, SMPD1 and MCOLN1 were significantly associated with LB pathology (p range: 0.03-4.14 x10(-5)). Overall, the mean levels of GCase activity were significantly lower in GBA mutation carriers compared to non-carriers (p<0.001). A significant increase and accumulation of several species for the lipid classes, ceramides and sphingolipids, was observed in LBD brains carrying GBA mutations compared to controls (p range: p<0.05-p<0.01).
Interpretation: Our study indicates that variants in GBA, SMPD1 and MCOLN1 are associated with LB pathology. Biochemical data comparing GBA mutation carrier to non-carriers support these findings, which have important implications for biomarker development and therapeutic strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- McKeith IG, Perry EK, Perry RH. Report of the second dementia with Lewy body international workshop: diagnosis and treatment. Consortium on Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neurology. 1999;53: 902–905. - PubMed
-
- McKeith IG. Clinical Lewy body syndromes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;920: 1–8. - PubMed
-
- McKeith IG. Spectrum of Parkinson's disease, Parkinson's dementia, and Lewy body dementia. Neurol Clin. 2000;18: 865–902. - PubMed
-
- Tayebi N, Walker J, Stubblefield B, Orvisky E, LaMarca ME, Wong K, et al. Gaucher disease with parkinsonian manifestations: does glucocerebrosidase deficiency contribute to a vulnerability to parkinsonism? Mol Genet Metab. 2003;79: 104–109. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Iseki E, Togo T, Yamaguchi A, Katsuse O, Katsuyama K, et al. Neuronal and glial accumulation of alpha- and beta-synucleins in human lipidoses. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114: 481–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

