Effect of cardiac arrest on cognitive impairment and hippocampal plasticity in middle-aged rats
- PMID: 25933411
- PMCID: PMC4416883
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124918
Effect of cardiac arrest on cognitive impairment and hippocampal plasticity in middle-aged rats
Abstract
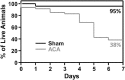
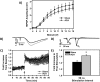
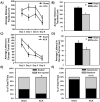
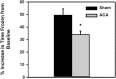
Cardiopulmonary arrest is a leading cause of death and disability in the United States that usually occurs in the aged population. Cardiac arrest (CA) induces global ischemia, disrupting global cerebral circulation that results in ischemic brain injury and leads to cognitive impairments in survivors. Ischemia-induced neuronal damage in the hippocampus following CA can result in the impairment of cognitive function including spatial memory. In the present study, we used a model of asphyxial CA (ACA) in nine month old male Fischer 344 rats to investigate cognitive and synaptic deficits following mild global cerebral ischemia. These experiments were performed with the goals of 1) establishing a model of CA in nine month old middle-aged rats; and 2) to test the hypothesis that learning and memory deficits develop following mild global cerebral ischemia in middle-aged rats. To test this hypothesis, spatial memory assays (Barnes circular platform maze and contextual fear conditioning) and field recordings (long-term potentiation and paired-pulse facilitation) were performed. We show that following ACA in nine month old middle-aged rats, there is significant impairment in spatial memory formation, paired-pulse facilitation n dysfunction, and a reduction in the number of non-compromised hippocampal Cornu Ammonis 1 and subiculum neurons. In conclusion, nine month old animals undergoing cardiac arrest have impaired survival, deficits in spatial memory formation, and synaptic dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- McNally B, Robb R, Mehta M, Vellano K, Valderrama AL, Yoon PW, et al. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest surveillance—Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival (CARES), United States, October 1, 2005—December 31, 2010. MMWR Surveillance summaries: Morbidity and mortality weekly report Surveillance summaries / CDC. 2011. July 29;60(8):1–19. . Epub 2011/07/29. eng. - PubMed
-
- Nichol G, Thomas E, Callaway CW, Hedges J, Powell JL, Aufderheide TP, et al. Regional variation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest incidence and outcome. JAMA: the journal of the American Medical Association. 2008. September 24;300(12):1423–31. PMCID: 3187919. Epub 2008/09/25. eng. 10.1001/jama.300.12.1423 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

