Effects of Low-Dose Bisphenol A on DNA Damage and Proliferation of Breast Cells: The Role of c-Myc
- PMID: 25933419
- PMCID: PMC4671234
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1409199
Effects of Low-Dose Bisphenol A on DNA Damage and Proliferation of Breast Cells: The Role of c-Myc
Abstract
Background: Humans are exposed to low-dose bisphenol A (BPA) through plastic consumer products and dental sealants containing BPA. Although a number of studies have investigated the mammary gland effects after high-dose BPA exposure, the study findings differ. Furthermore, there has been a lack of mechanistic studies.
Objective: The objective of this study was to investigate the effect and the mechanism of low-dose BPA in mammary gland cells.
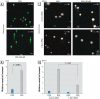
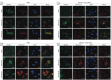
Methods: We evaluated DNA damage following BPA exposure using the comet assay and immunofluorescence staining, and used cell counting and three-dimensional cultures to evaluate effects on proliferation. We examined the expressions of markers of DNA damage and cell-cycle regulators by immunoblotting and performed siRNA-mediated gene silencing to determine the role of c-Myc in regulating BPA's effects.
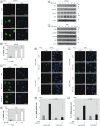
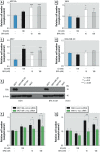
Results: Low-dose BPA significantly promoted DNA damage, up-regulated c-Myc and other cell-cycle regulatory proteins, and induced proliferation in parallel in estrogen receptor-α (ERα)-negative mammary cells. Silencing c-Myc diminished these BPA-induced cellular events, suggesting that c-Myc is essential for regulating effects of BPA on DNA damage and proliferation in mammary cells.
Conclusions: Low-dose BPA exerted c-Myc-dependent genotoxic and mitogenic effects on ERα-negative mammary cells. These findings provide significant evidence of adverse effects of low-dose BPA on mammary cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Examining BPA's Mechanisms of Action: The Role of c-Myc.Environ Health Perspect. 2015 Dec;123(12):A304. doi: 10.1289/ehp.123-A304. Environ Health Perspect. 2015. PMID: 26623713 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Audebert M, Dolo L, Perdu E, Cravedi JP, Zalko D. Use of the γH2AX assay for assessing the genotoxicity of bisphenol A and bisphenol F in human cell lines. Arch Toxicol. 2011;85:1463–1473. - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB. Initiating cellular stress responses. Cell. 2004;118:9–17. - PubMed
-
- Boyd M, Hildebrandt RH, Bartow SA. Expression of the estrogen receptor gene in developing and adult human breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;37:243–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
