Dosage compensation in Drosophila
- PMID: 25934013
- PMCID: PMC4448616
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a019398
Dosage compensation in Drosophila
Abstract
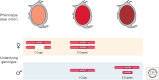
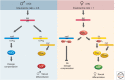
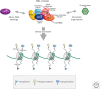
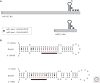
Dosage compensation in Drosophila increases the transcription of genes on the single X chromosome in males to equal that of both X chromosomes in females. Site-specific histone acetylation by the male-specific lethal (MSL) complex is thought to play a fundamental role in the increased transcriptional output of the male X. Nucleation and sequence-independent spreading of the complex to active genes serves as a model for understanding the targeting and function of epigenetic chromatin-modifying complexes. Interestingly, two noncoding RNAs are key for MSL assembly and spreading to active genes along the length of the X chromosome.
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
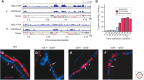
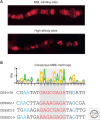
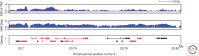
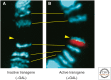

Similar articles
-
The structure-function link of compensated chromatin in Drosophila.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009 Dec;19(6):550-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.10.004. Epub 2009 Oct 31. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009. PMID: 19880310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetylated histone H4 on the male X chromosome is associated with dosage compensation in Drosophila.Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):96-104. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.96. Genes Dev. 1994. PMID: 8288132
-
Gene expression analysis of the function of the male-specific lethal complex in Drosophila.Genetics. 2005 Apr;169(4):2061-74. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.036020. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15716510 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic spreading of the Drosophila dosage compensation complex from roX RNA genes into flanking chromatin.Cell. 1999 Aug 20;98(4):513-22. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81979-0. Cell. 1999. PMID: 10481915
-
The right dose for every sex.Chromosoma. 2007 Apr;116(2):95-106. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0089-x. Epub 2006 Nov 24. Chromosoma. 2007. PMID: 17124606 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct mechanisms mediate X chromosome dosage compensation in Anopheles and Drosophila.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Jul 15;4(9):e202000996. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000996. Print 2021 Sep. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34266874 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic moonlighting: Catalytic-independent functions of histone modifiers in regulating transcription.Sci Adv. 2023 Apr 21;9(16):eadg6593. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg6593. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37083523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb-mediated repression of paternal chromosomes maintains haploid dosage in diploid embryos of Marchantia.Elife. 2022 Aug 23;11:e79258. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79258. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35996955 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and regulation of animal sex chromosomes.Nat Rev Genet. 2025 Jan;26(1):59-74. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00757-3. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Nat Rev Genet. 2025. PMID: 39026082 Review.
-
Long Noncoding RNAs-Crucial Players Organizing the Landscape of the Neuronal Nucleus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 27;22(7):3478. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073478. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33801737 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amrein H, Axel R. 1997. Genes expressed in neurons of adult male Drosophila. Cell 88: 459–469. - PubMed
WWW RESOURCES
-
- www.FlyBase.org A database of Drosophila genes and genomes.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
