Target activation by regulatory RNAs in bacteria
- PMID: 25934124
- PMCID: PMC4542691
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuv016
Target activation by regulatory RNAs in bacteria
Abstract
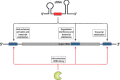
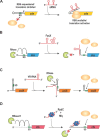
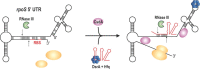
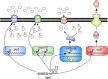
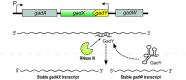
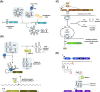
Bacterial small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs) are commonly known to repress gene expression by base pairing to target mRNAs. In many cases, sRNAs base pair with and sequester mRNA ribosome-binding sites, resulting in translational repression and accelerated transcript decay. In contrast, a growing number of examples of translational activation and mRNA stabilization by sRNAs have now been documented. A given sRNA often employs a conserved region to interact with and regulate both repressed and activated targets. However, the mechanisms underlying activation differ substantially from repression. Base pairing resulting in target activation can involve sRNA interactions with the 5(') untranslated region (UTR), the coding sequence or the 3(') UTR of the target mRNAs. Frequently, the activities of protein factors such as cellular ribonucleases and the RNA chaperone Hfq are required for activation. Bacterial sRNAs, including those that function as activators, frequently control stress response pathways or virulence-associated functions required for immediate responses to changing environments. This review aims to summarize recent advances in knowledge regarding target mRNA activation by bacterial sRNAs, highlighting the molecular mechanisms and biological relevance of regulation.
Keywords: Hfq; RNase E; anti-antisense; degradation interference; sRNA; sponge RNA.
© FEMS 2015. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Altuvia S, Weinstein-Fischer D, Zhang A, et al. A small, stable RNA induced by oxidative stress: role as a pleiotropic regulator and antimutator. Cell. 1997;90:43–53. - PubMed
-
- Antal M, Bordeau V, Douchin V, et al. A small bacterial RNA regulates a putative ABC transporter. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:7901–8. - PubMed
-
- Babitzke P, Romeo T. CsrB sRNA family: sequestration of RNA-binding regulatory proteins. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007;10:156–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

