MDC1 functionally identified as an androgen receptor co-activator participates in suppression of prostate cancer
- PMID: 25934801
- PMCID: PMC4446443
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv394
MDC1 functionally identified as an androgen receptor co-activator participates in suppression of prostate cancer
Abstract
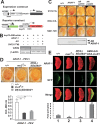
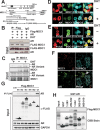
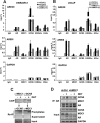
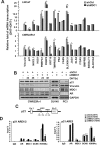
Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint protein 1 (MDC1) is essential for DNA damage response. However, the role of MDC1 in modulating gene transcription independently of DNA damage and the underlying mechanisms have not been fully defined. Androgen receptor (AR) is the central signaling pathway in prostate cancer (PCa) and its target genes are involved in both promotion and suppression of PCa. Here, we functionally identified MDC1 as a co-activator of AR. We demonstrate that MDC1 facilitates the association between AR and histone acetyltransferase GCN5, thereby increasing histone H3 acetylation level on cis-regulatory elements of AR target genes. MDC1 knockdown promotes PCa cells growth and migration. Moreover, depletion of MDC1 results in decreased expression of a subset of the endogenous androgen-induced target genes, including cell cycle negative regulator p21 and PCa metastasis inhibitor Vinculin, in AR positive PCa cell lines. Finally, the expression of MDC1 and p21 correlates negatively with aggressive phenotype of clinical PCa. These studies suggest that MDC1 as an epigenetic modifier regulates AR transcriptional activity and MDC1 may function as a tumor suppressor of PCa, and provide new insight into co-factor-AR-signaling pathway mechanism and a better understanding of the function of MDC1 on PCa.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

