Genome-wide association study of recalcitrant atopic dermatitis in Korean children
- PMID: 25935106
- PMCID: PMC4562879
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.030
Genome-wide association study of recalcitrant atopic dermatitis in Korean children
Abstract
Background: Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a heterogeneous chronic inflammatory skin disease. Most AD during infancy resolves during childhood, but moderate-to-severe AD with allergic sensitization is more likely to persist into adulthood and more often occurs with other allergic diseases.
Objective: We sought to find susceptibility loci by performing the first genome-wide association study (GWAS) of AD in Korean children with recalcitrant AD, which was defined as moderate-to-severe AD with allergic sensitization.
Methods: Our study included 246 children with recalcitrant AD and 551 adult control subjects with a negative history of both allergic disease and allergic sensitization. DNA from these subjects was genotyped; sets of common single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were imputed and used in the GWAS after quality control checks.
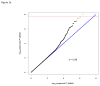
Results: SNPs at a region on 13q21.31 were associated with recalcitrant AD at a genome-wide threshold of significance (P < 2.0 × 10(-8)). These associated SNPs are more than 1 Mb from the closest gene, protocadherin (PCDH)9. SNPs at 4 additional loci had P values of less than 1 × 10(-6), including SNPs at or near the neuroblastoma amplified sequence (NBAS; 2p24.3), thymus-expressed molecule involved in selection (THEMIS; 6q22.33), GATA3 (10p14), and S-phase cyclin A-associated protein in the ER (SCAPER; 15q24.3) genes. Further analysis of total serum IgE levels suggested 13q21.31 might be primarily an IgE locus, and analyses of published data demonstrated that SNPs at the 15q24.3 region are expression quantitative trait loci for 2 nearby genes, ISL2 and proline-serine-threonine phosphatase interacting protein 1 (PSTPIP1), in immune cells.
Conclusion: Our GWAS of recalcitrant AD identified new susceptibility regions containing genes involved in epithelial cell function and immune dysregulation, 2 key features of AD, and potentially extend our understanding of their role in pathogenesis.
Keywords: Genome-wide association study; IgE; allergic sensitization; atopic dermatitis; children; severity.
Copyright © 2015 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none
Figures


Similar articles
-
A variant on chromosome 2p13.3 is associated with atopic dermatitis in Chinese Han population.Gene. 2017 Sep 10;628:281-285. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.07.059. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28739399
-
A genome-wide association study of atopic dermatitis identifies loci with overlapping effects on asthma and psoriasis.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Dec 1;22(23):4841-56. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt317. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23886662 Free PMC article.
-
A Common Variant at 11q23.3 Is Associated with Susceptibility to Atopic Dermatitis in the Han Chinese Population.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021 Oct;25(10):638-645. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2020.0335. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 34609929
-
The Genetics and Epigenetics of Atopic Dermatitis-Filaggrin and Other Polymorphisms.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Dec;51(3):315-328. doi: 10.1007/s12016-015-8508-5. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26385242 Review.
-
Atopic dermatitis and autoimmunity: the occurrence of autoantibodies and their association with disease severity.Arch Dermatol Res. 2019 Apr;311(3):141-162. doi: 10.1007/s00403-019-01890-4. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Arch Dermatol Res. 2019. PMID: 30798353 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proteomics as a tool to improve novel insights into skin diseases: what we know and where we should be going.Front Surg. 2022 Oct 21;9:1025557. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1025557. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36338621 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation in Themis contributes to anaphylaxis severity following oral peanut challenge in CC027 mice.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Aug;154(2):387-397. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.03.027. Epub 2024 Apr 24. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38670234 Free PMC article.
-
Age-of-onset information helps identify 76 genetic variants associated with allergic disease.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jun 30;16(6):e1008725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008725. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32603359 Free PMC article.
-
IgE and IgG Anti-Thyroid Autoantibodies in Chinese Patients With Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria and a Literature Review.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022 Jan;14(1):131-142. doi: 10.4168/aair.2022.14.1.131. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 34983113 Free PMC article.
-
Themis controls T cell activation, effector functions, and metabolism of peripheral CD8+ T cells.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Sep 22;6(12):e202302156. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302156. Print 2023 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37739454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1483–94. - PubMed
-
- Ring J, Alomar A, Bieber T, Deleuran M, Fink-Wagner A, Gelmetti C, et al. Guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) Part II. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1176–93. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein P, Svartengren M. Genes, environments, and sex: factors of importance in atopic diseases in 7–9-year-old Swedish twins. Allergy. 1997;52:1079–86. - PubMed
-
- Nystad W, Roysamb E, Magnus P, Tambs K, Harris JR. A comparison of genetic and environmental variance structures for asthma, hay fever and eczema with symptoms of the same diseases: a study of Norwegian twins. Int J Epidemiol. 2005;34:1302–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

