Community challenges in biomedical text mining over 10 years: success, failure and the future
- PMID: 25935162
- PMCID: PMC4719069
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbv024
Community challenges in biomedical text mining over 10 years: success, failure and the future
Abstract
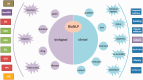
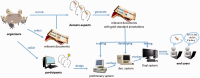
One effective way to improve the state of the art is through competitions. Following the success of the Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction (CASP) in bioinformatics research, a number of challenge evaluations have been organized by the text-mining research community to assess and advance natural language processing (NLP) research for biomedicine. In this article, we review the different community challenge evaluations held from 2002 to 2014 and their respective tasks. Furthermore, we examine these challenge tasks through their targeted problems in NLP research and biomedical applications, respectively. Next, we describe the general workflow of organizing a Biomedical NLP (BioNLP) challenge and involved stakeholders (task organizers, task data producers, task participants and end users). Finally, we summarize the impact and contributions by taking into account different BioNLP challenges as a whole, followed by a discussion of their limitations and difficulties. We conclude with future trends in BioNLP challenge evaluations.
Keywords: BioNLP challenges; BioNLP shared tasks; biomedical natural language processing (BioNLP); critical assessment; text mining.
Published by Oxford University Press 2015. This work is written by US Government employees and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

