Epidemiology of pediatric hand fractures presenting to a university hospital in Central Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 25935180
- PMCID: PMC4436756
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2015.5.10527
Epidemiology of pediatric hand fractures presenting to a university hospital in Central Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the epidemiology of pediatric hand fractures and to provide recommendations regarding prevention.
Methods: Medical records and x-rays were retrospectively reviewed for age at the time of injury, gender, fracture pattern, place where the injury occurred, and mechanism of injury. The study was conducted at King Khalid University Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia between January 2005 and December 2011.
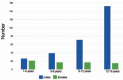
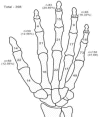
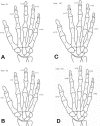
Results: Of 361 cases reviewed, there were 291 (80.6%) male and 70 (19.4%) female patients. Most (46.2%) were in the age group of 13-18 years. For age group 1-4 years, the most common place of occurrence was at home (81.3%) and for the group 13-18 years, outdoors was the place of occurrence (64.7%). Females were mostly injured at home while males had similar distribution of indoor and outdoor injuries. The most common causes of fractures were: door slams in the 1-8 years age group; falls at home, in the 9-12 years age group; and both falls at home and sports in the oldest age group (13-18 years). The little finger ray are the most frequently injured part of the hand followed by the middle finger.
Conclusion: Our series showed that most hand fractures in children occurred at home, which requires reevaluation of home settings. Implementation of safety measures during sports activities are relevant in the oldest age group.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiology of hand fractures at a tertiary care setting in Saudi Arabia.Saudi Med J. 2019 Jul;40(7):732-736. doi: 10.15537/smj.2019.7.24286. Saudi Med J. 2019. PMID: 31287136 Free PMC article.
-
Hand injuries in children at King Fahd Hospital of the University in Saudi Arabia (1989-1991).Afr J Med Med Sci. 2000 Sep-Dec;29(3-4):289-91. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2000. PMID: 11714008
-
Pattern of hand injuries in children and adolescents in a teaching hospital in Abha, Saudi Arabia.J R Soc Promot Health. 2001 Mar;121(1):47-9. doi: 10.1177/146642400112100110. J R Soc Promot Health. 2001. PMID: 11329697
-
A prospective study of pediatric hand fractures and review of the literature.Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014 May;30(5):299-304. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000000118. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014. PMID: 24759492 Review.
-
Pediatric Hand and Wrist Fractures.Clin Plast Surg. 2019 Jul;46(3):425-436. doi: 10.1016/j.cps.2019.02.012. Clin Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 31103087 Review.
Cited by
-
Hand Injuries in the Polish Silesian Paediatric Population-An Exploratory Cross-Sectional Study of Post-Traumatic X-rays.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Oct 20;56(10):550. doi: 10.3390/medicina56100550. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 33092076 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical and Nonsurgical Pediatric Hand Fractures: A Cohort Study.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020 Mar 25;8(3):e2703. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002703. eCollection 2020 Mar. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020. PMID: 32537358 Free PMC article.
-
The Pattern of Unintentional Injuries and Poisoning Among Children Admitted to King Abdulaziz Medical City, Jeddah, From 2014 to 2018 in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2022 Oct 19;14(10):e30484. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30484. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36415404 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency, Pattern, and Treatment of Hand Fractures in Children and Adolescents: A 27-Year Review of 4356 Pediatric Hand Fractures.Hand (N Y). 2022 Jan;17(1):92-97. doi: 10.1177/1558944719900565. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Hand (N Y). 2022. PMID: 32036680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morbidity Patterns of Non-Traffic Unintentional Injuries Among the Pediatric Age Group Attending the Emergency Department at King Abdul-Aziz Medical City, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2020 Jul 18;12(7):e9258. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9258. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32821604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonge O, Hyder AA. Reducing the global burden of childhood unintentional injuries. Arch Dis Childhood. 2014;99:62–69. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. The global burden of disease: 2004 update. Geneva (CH): World Health Organization; 2008.
-
- Vadivelu R, Dias JJ, Burke FD, Stanton J. Hand injuries in children: a prospective study. J Pediat Orthop. 2006;26:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Nofsinger CC, Wolfe SW. Common pediatric hand fractures. Curr Opinion Pediat. 2002;14:42–45. - PubMed
-
- Beris AE, Lykissas MG, Korompilias AV, Mitsionis GI, Vekris MD, Kostas-Agnantis IP. Digit and hand replantation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130:1141–1147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
