Proprioceptive feedback contributes to the adaptation toward an economical gait pattern
- PMID: 25935689
- PMCID: PMC7167590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2015.04.024
Proprioceptive feedback contributes to the adaptation toward an economical gait pattern
Abstract
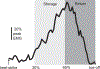
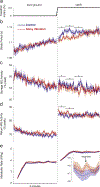
Humans generally prefer gait patterns with a low metabolic cost, but it is unclear how such patterns are chosen. We have previously proposed that humans may use proprioceptive feedback to identify economical movement patterns. The purpose of the present experiments was to investigate the role of plantarflexor proprioception in the adaptation toward an economical gait pattern. To disrupt proprioception in some trials, we applied noisy vibration (randomly varying between 40-120Hz) over the bilateral Achilles tendons while participants stood quietly or walked on a treadmill. For all 10min walking trials, the treadmill surface was initially level before slowly increasing to a 2.5% incline midway through the trial without participant knowledge. During standing posture, noisy vibration increased sway, indicating decreased proprioception accuracy. While walking on a level surface, vibration did not significantly influence stride period or metabolic rate. However, vibration had clear effects for the first 2-3min after the incline increase; vibration caused participants to walk with shorter stride periods, reduced medial gastrocnemius (MG) activity during mid-stance (30-65% stance), and increased MG activity during late-stance (65-100% stance). Over time, these metrics gradually converged toward the gait pattern without vibration. Likely as a result of this delayed adaptation to the new mechanical context, the metabolic rate when walking uphill was significantly higher in the presence of noisy vibration. These results may be explained by the disruption of proprioception preventing rapid identification of muscle activation patterns which allow the muscles to operate under favorable mechanical conditions with low metabolic demand.
Keywords: Gait adaptation; Metabolic cost; Muscle activity; Tendon vibration.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
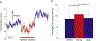
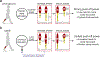
References
-
- Ainslie PN, Duffin J, 2009. Integration of cerebrovascular CO2 reactivity and chemoreflex control of breathing: mechanisms of regulation, measurement, and interpretation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol 296, R1473–R1495. - PubMed
-
- Alexander RM, 2002. Energetics and optimization of human walking and running: the 2000 Raymond Pearl memorial lecture. Am. J. Hum. Biol 14, 641–648. - PubMed
-
- Brockway JM, 1987. Derivation of formulae used to calculate energy expenditure in man. Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr 41, 463–471. - PubMed
-
- Chow CC, Imhoff TT, Collins JJ, 1998. Enhancing aperiodic stochastic resonance through noise modulation. Chaos 8, 616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

