Alternative modulation of protein-protein interactions by small molecules
- PMID: 25935873
- PMCID: PMC4728186
- DOI: 10.1016/j.copbio.2015.04.006
Alternative modulation of protein-protein interactions by small molecules
Abstract
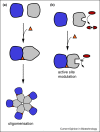
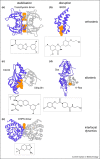
Protein-protein interactions (PPI) have become increasingly popular drug targets, with a number of promising compounds currently in clinical trials. Recent research shows, that PPIs can be modulated in more ways than direct inhibition, where novel non-competitive modes of action promise a solution for the difficult nature of PPI drug discovery. Here, we review recently discovered PPI modulators in light of their mode of action and categorise them as disrupting versus stabilising, orthosteric versus allosteric and by their ability to affect the proteins' dynamics. We also give recent examples of compounds successful in the clinic, analyse their physicochemical properties and discuss how to overcome the hurdles in discovering alternative modes of modulation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Koh G.C.K.W., Porras P., Aranda B., Hermjakob H., Orchard S.E. Analyzing protein–protein interaction networks. J Proteome Res. 2012;11:2014–2031. - PubMed
-
Extensive theoretical overview and tutorial on PPI networks and analysis with explanation of available experimental and computational tools and databases, as well as practical applications.
-
- Giordanetto F., Schäfer A., Ottmann C. Stabilization of protein–protein interactions by small molecules. Drug Discov Today. 2014;8:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Arkin M.R., Tang Y., Wells J.A. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein–protein interactions: progressing toward the reality. Chem Biol. 2014;21:1102–1114. - PMC - PubMed
-
Categorises PPIs according to the interface-complexity, gives examples and evaluates progress in the PPI drug discovery field over the past decade.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

